Ophthalmic immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 37033964
- PMCID: PMC10076523
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130238
Ophthalmic immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy and to report the clinical features, management, and outcomes of ophthalmic irAEs.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients who received ICI therapy from January 2016 to September 2022 at Peking Union Medical College Hospital and analyzed the incidence of systemic and ophthalmic adverse effects of this therapy.
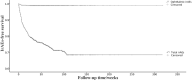
Results: Of 962 patients, 248 (25.8%) experienced irAEs. The first-year incidences of total irAEs and ophthalmic irAEs were 23.5% and 1.1%. The most common ICI received by the patients was pembrolizumab (373; 38.8%). Nearly half of the patients (477; 49.6%) had lung cancer. Combination therapy was associated with an increased incidence of irAEs without statistical significance. Patients with lung cancer presented with an increased incidence of total irAEs (p = 0.003) and ophthalmic irAEs (p = 0.032). Eleven patients had ophthalmic manifestations, including ophthalmoplegia (6/11), conjunctivitis (3/11), reactive cutaneous capillary endothelial proliferation (RCCEP) (1/11), and orbital inflammation (1/11). Eight patients had concomitant extra-ophthalmic irAEs. Furthermore, ICIs were discontinued in nine patients, and most ophthalmic manifestations were well controlled with topical and systemic steroids. Ten patients were treated with intravenous or oral steroids. However, cancer progression occurred in five out of eleven patients after the interruption of ICIs.
Conclusion: IrAEs are correlated with ICI regimens and underlying neoplasia. In our Chinese cohort, patients have a higher risk of ophthalmoplegia than uveitis. Early recognition and multidisciplinary consultation are crucial for optimal treatment of ophthalmic irAEs.
Keywords: adverse events; immune checkpoint inhibitor; incidence; inflammation; ophthalmic.
Copyright © 2023 Gan, Chen, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ocular Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 24;12:701951. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.701951. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34504488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk of Ophthalmic Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2022 Aug;30(6):1449-1459. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2021.1890133. Epub 2021 May 10. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 33970759
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Rechallenge Safety and Efficacy in Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients After Immune-Related Adverse Events.Clin Lung Cancer. 2022 Dec;23(8):686-693. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2022.07.015. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Clin Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36050243
-
Ophthalmic Immune-Related Adverse Events after Anti-CTLA-4 or PD-1 Therapy Recorded in the American Academy of Ophthalmology Intelligent Research in Sight Registry.Ophthalmology. 2021 Jun;128(6):910-919. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Ophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 33166553
-
Safety and Efficacy Outcomes in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Treated Patients With Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Requiring Treatment Interruption or Discontinuation Due to Immune-Related Adverse Events.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2024 Apr;22(2):368-379. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2023.12.007. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38245437
Cited by
-
Immune Checkpoints and Graves' Disease, Thyroid Eye Disease, and Orbital Myopathy: A Comprehensive Review.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2024 Sep 16;19(3):368-380. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v19i3.15047. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2024. PMID: 39359534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosing and Managing Uveitis Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;14(3):336. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030336. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ophthalmic Immune-Related Adverse Events and Association with Survival: Results From a Real-World Database.Am J Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec;268:348-359. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2024.08.044. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Am J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39271090
-
Consensus disease definitions for ophthalmic immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Apr 8;13(4):e011049. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-011049. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40199607 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal ulcer development due to sintilimab-anlotinib combination therapy-induced dry eye: a case report.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 May 31;13(5):2571-2579. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1952. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38881937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun MM, Kelly SP, Mylavarapu Bs AL, Holland GN, Coleman AL, Yu F, et al. . Ophthalmic immune-related adverse events after anti-CTLA-4 or PD-1 therapy recorded in the American academy of ophthalmology intelligent research in sight registry. Ophthalmology (2021) 128(6):910–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.11.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical