Convergent antibody responses are associated with broad neutralization of hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 37033983
- PMCID: PMC10080129
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135841
Convergent antibody responses are associated with broad neutralization of hepatitis C virus
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Convergent antibody responses are associated with broad neutralization of hepatitis C virus.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 25;14:1201033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1201033. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37180140 Free PMC article.
Abstract
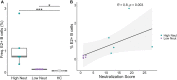
Introduction: Early development of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) targeting the hepatitis C virus (HCV) envelope glycoprotein E2 is associated with spontaneous clearance of infection, so induction of bNAbs is a major goal of HCV vaccine development. However, the molecular antibody features important for broad neutralization are not known.
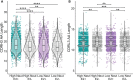
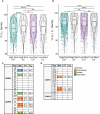
Methods: To identify B cell repertoire features associated with broad neutralization, we performed RNA sequencing of the B cell receptors (BCRs) of HCV E2-reactive B cells of HCV-infected individuals with either high or low plasma neutralizing breadth. We then produced a monoclonal antibody (mAb) expressed by pairing the most abundant heavy and light chains from public clonotypes identified among clearance, high neutralization subjects.
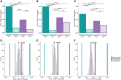
Results: We found distinctive BCR features associated with broad neutralization of HCV, including long heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 (CDRH3) regions, specific VH gene usage, increased frequencies of somatic hypermutation, and particular VH gene mutations. Most intriguing, we identified many E2-reactive public BCR clonotypes (heavy and light chain clones with the same V and J-genes and identical CDR3 sequences) present only in subjects who produced highly neutralizing plasma. The majority of these public clonotypes were shared by two subjects who cleared infection. A mAb expressing the most abundant public heavy and light chains from these clearance, high neutralization subjects had features enriched in high neutralization clonotypes, such as increased somatic hypermutation frequency and usage of IGHV1-69, and was cross-neutralizing.
Discussion: Together, these results demonstrate distinct BCR repertoires associated with high plasma neutralizing capacity. Further characterization of the molecular features and function of these antibodies can inform HCV vaccine development.
Keywords: B cell; B cell receptor; hepatitis C virus; neutralizing antibody; vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 Skinner, Ogega, Frumento, Clark, Yegnasubramanian, Schuebel, Meyers, Gupta, Wheelan, Cox, Crowe, Ray and Bailey.
Conflict of interest statement
JC has served as a consultant for Luna Labs USA, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corporation, Emergent Biosolutions, GlaxoSmithKline and BTG International Inc, is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Meissa Vaccines, a former member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Gigagen Grifols and is founder of IDBiologics. The laboratory of JC received unrelated sponsored research agreements from AstraZeneca, Takeda, and IDBiologics during the conduct of the study. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization . Hepatitis c (2021). Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

