Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
- PMID: 37034122
- PMCID: PMC10079507
- DOI: 10.12793/tcp.2023.31.e4
Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Abstract
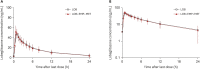
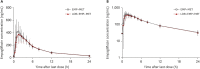
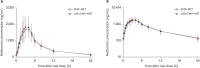
Concomitant administration of lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin is expected to enhance blood glucose-lowering effects and improve medication compliance in patients with diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated the pharmacokinetic (PK) interactions and safety of lobeglitazone and co-administered empagliflozin and metformin, which are approved agents used in clinical settings. Two randomized, open-label, multiple-dose, 2-treatment, 2-period, 2-sequence crossover clinical trials (parts 1 and 2) were conducted independently. In part 1, lobeglitazone monotherapy or lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin triple therapy was administered for 5 days. In part 2, empagliflozin and metformin dual therapy or the abovementioned triple therapy were administered for 5 days. Serial blood samples were collected up to 24 hours after the last dose in each period for PK evaluation. The primary PK parameters (AUCtau,ss, Cmax,ss) of treatment regimens in each study part were calculated and compared. For lobeglitazone, the geometric mean ratios (GMRs) with 90% confidence intervals (CI) for triple therapy over monotherapy were 1.08 (1.03-1.14) for Cmax,ss and 0.98 (0.90-1.07) for AUCtau,ss. For empagliflozin, the GMRs and 90% CIs for triple therapy over dual therapy were 0.87 (0.78-0.97) for Cmax,ss and 0.97 (0.93-1.00) for AUCtau,ss. For metformin, the GMRs and 90% CIs for triple therapy over dual therapy were 1.06 (0.95-1.17) for Cmax,ss and 1.04 (0.97-1.12) for AUCtau,ss. All reported adverse events were mild. The triple therapy consisting of lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin did not show any clinically relevant drug interactions in relation to the PKs and safety of each drug substance.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04334213.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus; Drug Interactions; Pharmacokinetics; Thiazolidinediones.
Copyright © 2023 Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: - Authors: Nothing to declare - Reviewers: Nothing to declare - Editors: Nothing to declare
Figures
Similar articles
-
No Relevant Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interaction Between the Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin and Lobeglitazone, a Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Agonist, in Healthy Subjects.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Apr 28;15:1725-1734. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S302215. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33953542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of the pharmacokinetics of co-administered metformin and lobeglitazone, a thiazolidinedione antihyperglycemic agent, in healthy subjects.Curr Med Res Opin. 2012 Jul;28(7):1213-20. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2012.703131. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012. PMID: 22697273 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic Interaction Between Amlodipine and Lobeglitazone, a Novel Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-γ Agonist, in Healthy Subjects.Clin Ther. 2015 Sep;37(9):1999-2006.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 26163202 Clinical Trial.
-
Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422060-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. PMID: 15099124 Review.
-
Drug interactions of clinical importance with antihyperglycaemic agents: an update.Drug Saf. 2005;28(7):601-31. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200528070-00004. Drug Saf. 2005. PMID: 15963007 Review.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45:S1–S2. - PubMed
-
- Korean Diabetes Association. 2021 diabetes treatment guideline. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2021.
-
- Foretz M, Guigas B, Viollet B. Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15:569–589. - PubMed
-
- Frampton JE. Empagliflozin: a review in type 2 diabetes. Drugs. 2018;78:1037–1048. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
