Characteristics of culprit intracranial plaque without substantial stenosis in ischemic stroke using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 37034175
- PMCID: PMC10076565
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1160018
Characteristics of culprit intracranial plaque without substantial stenosis in ischemic stroke using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Background and aims: We aim to analyze the difference in quantitative features between culprit and non-culprit intracranial plaque without substantial stenosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall MRI (3D hr-vw-MRI).
Methods: The patients with cerebral ischemic symptoms of the unilateral anterior circulation were recruited who had non-stenotic intracranial atherosclerosis (<50%) confirmed by computed tomographic angiographic (CTA) or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). All patients underwent 3D hr-vw MRI within 1 month after symptom onset. 3D hr-vw-MRI characteristics, including wall thickness, plaque burden, enhancement ratio, plaque volume and intraplaque hemorrhage, and histogram features were analyzed based on T2-, precontrast T1-, and post-contrast T1-weighted images. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to identify key determinates differentiating culprit and non-culprit plaques and to calculate the odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
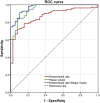
Results: A total of 150 plaques were identified, of which 133 plaques (97 culprit and 36 non-culprit) were in the middle cerebral artery, three plaques (all culprit) were in the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and 14 (11 culprit and three non-culprit) were in the internal carotid artery (ICA). Of all the quantitative parameters analyzed, plaque volume, maximum wall thickness, minimum wall thickness, plaque burden, enhancement ratio, coefficient of variation of the most stenotic site, enhancement ratio of whole culprit plaque in culprit plaques were significantly higher than those in non-culprit plaques. Multivariate logistic regression analysis found that plaque volume [OR, 1.527 (95% CI, 1.231-1.894); P < 0.001] and enhancement ratio of whole plaque [OR, 1.095 (95% CI, 1.021-1.175); P = 0.011] were significantly associated with culprit plaque. The combination of the two features obtained a better diagnostic efficacy for culprit plaque with sensitivity and specificity (0.910 and 0.897, respectively) than each of the two parameters alone.
Conclusion: 3D hr-vw MRI features of intracranial atherosclerotic plaques provided potential values over prediction of ischemic stroke patients with non-stenotic arteries. The plaque volume and enhancement ratio of whole plaque of stenosis site were found to be effective predictive parameters.
Keywords: 3D high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging; diagnostic efficacy; histogram features; intracranial non-stenotic atherosclerotic plaques; ischemic stroke.
Copyright © 2023 Tian, Shi, Wang, Xu, Peng, Zhang, Liu, Chen, Tian, Lu and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative Histogram Analysis on Intracranial Atherosclerotic Plaques: A High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.Stroke. 2020 Jul;51(7):2161-2169. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029062. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Stroke. 2020. PMID: 32568660 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Features of Culprit Intracranial Atherosclerotic Lesions: A Whole-Brain Vessel Wall Imaging Study in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Jul 22;7(15):e009705. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009705. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30033434 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial Atherosclerotic Plaque Characteristics and Burden Associated With Recurrent Acute Stroke: A 3D Quantitative Vessel Wall MRI Study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 28;13:706544. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.706544. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34393761 Free PMC article.
-
Culprit intracranial plaque without substantial stenosis in acute ischemic stroke on vessel wall MRI: A systematic review.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Aug;287:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.06.907. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 31254918 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Therapeutic Response to Statin Therapy in Patients With Intracranial or Extracranial Carotid Atherosclerosis by Vessel Wall MRI: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Oct 27;8:742935. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.742935. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34778404 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anatomical location-related hemodynamic variations are associated with atherosclerosis in the middle cerebral artery: a preliminary cross-sectional 4D flow and 3D vessel wall MRI study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Apr 1;15(4):3585-3601. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1733. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40235780 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative plaque characteristics based on 3D high-resolution vessel wall imaging predict long-term recurrence in intracranial atherosclerotic stroke.Neuroradiology. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.1007/s00234-025-03642-w. Online ahead of print. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 40536671 No abstract available.
-
What are we talking about when we talk about plaque burden: is that enough to find associations with recurrent ischemic stroke?Eur Radiol. 2024 May;34(5):3019-3021. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10365-0. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37889275 No abstract available.
References
-
- Huang J., Jiao S., Zhao X., Zhang J., Zhang C., Chen M., et al. (2019). Characteristics of patients with enhancing intracranial atherosclerosis and association between plaque enhancement and recent cerebrovascular ischemic events: A high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Acta Radiol. 60 1301–1307. 10.1177/0284185118822645 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lu S. S., Ge S., Su C. Q., Xie J., Shi H. B., Hong X. N. (2018). Plaque distribution and characteristics in low-grade middle cerebral artery stenosis and its clinical relevance: A 3-dimensional high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 27 2243–2249. 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.04.010 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

