Deubiquitinase USP33 promotes the glycolysis and growth of osteosarcoma by modifying PFKFB3 ubiquitination and degradation
- PMID: 37034227
- PMCID: PMC10077048
Deubiquitinase USP33 promotes the glycolysis and growth of osteosarcoma by modifying PFKFB3 ubiquitination and degradation
Abstract
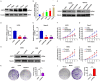
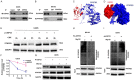
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common malignant tumor of the bone tissue with the lowest survival rate among all pediatric cancers. OS cells grow vigorously under malnutrition; however, the mechanism by which they adapt to metabolic stress via metabolic reprogramming remains undefined. Here, we demonstrated that USP33, a member of the DUBs family, was significantly upregulated in the tissues of patients with OS compared to normal tissues. Moreover, high USP33 expression was significantly associated with poor survival. Functional assays suggested that USP33 promoted OS cell growth through the induction of aerobic glycolysis. Additionally, we confirmed that 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) was critical for USP33-induced proliferation and aerobic glycolysis in OS cells, and the protein expression levels of PFKFB3 and USP33 were positively correlated in the OS tissues. Mechanistically, USP33 stabilized the expression of PFKFB3 by suppressing the ubiquitin mediated PFKFB3 degradation. Collectively, these findings reveal a mechanism by which OS cells survive in a dystrophic tumor microenvironment, with the USP33-PFKFB3 axis as a critical driver of aerobic glycolysis and OS proliferation. Furthermore, these findings reveal novel insights into the adaptation of cancer cells to metabolic stress in OS.
Keywords: Osteosarcoma; PFKFB3; USP33; deubiquitinase; ubiquitination.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin-like protein FAT10 promotes osteosarcoma glycolysis and growth by upregulating PFKFB3 via stabilization of EGFR.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 1;10(7):2066-2082. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32775001 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK2 promotes osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by modifying PFKFB3 ubiquitination and degradation.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Dec 15;385(2):111689. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111689. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31678169
-
miR-26b inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis induction via the downregulation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 driven glycolysis in osteosarcoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2015 Apr;33(4):1890-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3797. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25672572
-
6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 and 4: A pair of valves for fine-tuning of glucose metabolism in human cancer.Mol Metab. 2019 Feb;20:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30553771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuances of PFKFB3 Signaling in Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2022 Jun;22(4):e604-e614. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Clin Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35135735 Review.
Cited by
-
USP33 facilitates the ovarian cancer progression via deubiquitinating and stabilizing CBX2.Oncogene. 2024 Oct;43(43):3170-3183. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03151-9. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39256572
-
RNA binding protein ELAVL1-mediated USP33 stabilizes HIF1A to promote pathological proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of RECs.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep 25;44(1):393. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03311-6. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39320536
-
Lung-Targeted Lipid Nanoparticle-Delivered siUSP33 Attenuates SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Virulence by Promoting Envelope Degradation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(42):e2406211. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406211. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39301916 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the SphK1/S1P/PFKFB3 axis suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by disrupting glycolytic energy supply that drives tumor angiogenesis.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 10;22(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04830-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38200582 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Deubiquitinating Enzymes in Primary Bone Cancer.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;67(8):3027-3040. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01254-y. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39177860 Review.
References
-
- Zhang H, Wang J, Ren T, Huang Y, Liang X, Yu Y, Wang W, Niu J, Guo W. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting TRA2B. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:54–65. - PubMed
-
- Williams SA, Maecker HL, French DM, Liu J, Gregg A, Silverstein LB, Cao TC, Carano RA, Dixit VM. USP1 deubiquitinates ID proteins to preserve a mesenchymal stem cell program in osteosarcoma. Cell. 2011;146:918–930. - PubMed
-
- Pierce TT, Shailam R, Lozano-Calderon S, Sagar P. Inter-rater variability in the interpretation of pre and post contrast MRI for pre-surgical evaluation of osteosarcoma in long bones in pediatric patients and young adults. Surg Oncol. 2019;28:135–139. - PubMed
-
- Baclesse F. Osteosarcoma of the long bones in young persons; radiodiagnosis and therapy. Brux Med. 1952;32:2599–2612. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
