An in-silico approach leads to explore six genes as a molecular signatures of lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37034228
- PMCID: PMC10077044
An in-silico approach leads to explore six genes as a molecular signatures of lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
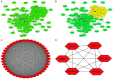
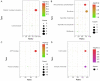
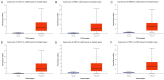
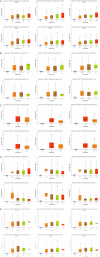
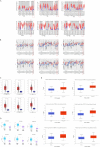
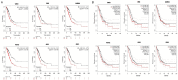
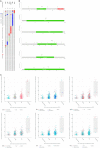
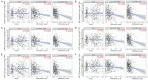
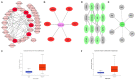
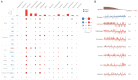
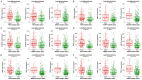
Due to heterogenetic-specific nature of the available biomarkers, the incidence of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is on the rise worldwide. Previously reported LUAD-related hub genes were searched from the medical literature via literature mining and were processed to identify few top genes via degree method. Later, a comprehensive in silico methodology was applied on the selected real hub genes to identify their tumor driving, diagnostic, and prognostic roles in LUAD patients with divers clinicopathological variables. Out of total 145 extracted hub genes, six genes including CDC6, PBK, AURKA, KIF2C, OIP5, and PRC1 were identified as real hub genes. The expression analysis showed that all these genes were significantly up-regulated across LUAD samples of different clinicopathological variables. In addition, a variety of unique correlations among the expression and of real hub genes and some other parameters including promoter methylation status, overall survival (OS), genetic changes, tumor purity, and immune cell infiltration have also been explored in the present study. Moreover, via TFS-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network, one important TF (E2F1) and one important miRNAs (hsa-mir-34a-5p) that targeted all the real hub genes were also identified. Finally, a variety of drugs also predicted to be very useful in treating LUAD. The discovery of the real hub genes, TFS-miRNA-mRNA network, and chemotherapeutic drugs associated with LUAD provides new insights into underlying mechanisms and treatment of LUAD overcoming heterogeneity barriers.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma; PubMed; biomarker; hub gene; miRNA.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening a novel six critical gene-based system of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in prostate adenocarcinoma patients with different clinical variables.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jun 15;14(6):3658-3682. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35836886 Free PMC article.
-
Identification key genes, key miRNAs and key transcription factors of lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):1917-1933. doi: 10.21037/jtd-19-4168. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642095 Free PMC article.
-
Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of colorectal cancer: Capable to overcome the heterogeneity-specific barrier and valid for global applications.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 2;16(9):e0256020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256020. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34473751 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative bioinformatics and RNA sequencing based methodology results in the exploration of breast invasive carcinoma biomarkers.Am J Transl Res. 2023 May 15;15(5):3067-3091. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37303632 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and Validating a Novel miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network Associated with Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Chin Med Sci J. 2022 Mar 31;37(1):31-43. doi: 10.24920/003966. Chin Med Sci J. 2022. PMID: 35531948
Cited by
-
MIS18A upregulation promotes cell viability, migration and tumor immune evasion in lung adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jun 13;28(2):376. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14509. eCollection 2024 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38910901 Free PMC article.
-
KIF2C/MCAK a prognostic biomarker and its oncogenic potential in malignant progression, and prognosis of cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis as biomarker.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2024 Sep;61(6):404-434. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2024.2309933. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2024. PMID: 38344808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
