Laryngeal Imaging Study of Glottal Attack/Offset Time in Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia during Connected Speech
- PMID: 37034315
- PMCID: PMC10077958
- DOI: 10.3390/app13052979
Laryngeal Imaging Study of Glottal Attack/Offset Time in Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia during Connected Speech
Abstract
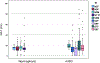
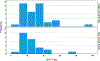
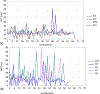
Adductor spasmodic dysphonia (AdSD) disrupts laryngeal muscle control during speech and, therefore, affects the onset and offset of phonation. In this study, the goal is to use laryngeal high-speed videoendoscopy (HSV) to measure the glottal attack time (GAT) and glottal offset time (GOT) during connected speech for normophonic (vocally normal) and AdSD voices. A monochrome HSV system was used to record readings of six CAPE-V sentences and part of the "Rainbow Passage" from the participants. Three raters visually analyzed the HSV data using a playback software to measure the GAT and GOT. The results show that the GAT was greater in the AdSD group than in the normophonic group; however, the clinical significance of the amount of this difference needs to be studied further. More variability was observed in both GATs and GOTs of the disorder group. Additionally, the GAT and GOT time series were found to be nonstationary for the AdSD group while they were stationary for the normophonic voices. This study shows that the GAT and GOT measures can be potentially used as objective markers to characterize AdSD. The findings will potentially help in the development of standardized measures for voice evaluation and the accurate diagnosis of AdSD.
Keywords: adductor spasmodic dysphonia; connected speech; glottal attack time; glottal offset time; high-speed videoendoscopy; laryngeal imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Study of Glottal Attack Time and Glottal Offset Time in Neurogenic Voice Disorders During Sustained Phonation.J Voice. 2025 Mar 18:S0892-1997(25)00077-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2025.02.030. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 40107936
-
Deep-Learning-Based Representation of Vocal Fold Dynamics in Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia during Connected Speech in High-Speed Videoendoscopy.J Voice. 2025 Mar;39(2):570.e1-570.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2022.08.022. Epub 2022 Sep 23. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 36154973
-
Detection of Vocal Fold Image Obstructions in High-Speed Videoendoscopy During Connected Speech in Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia: A Convolutional Neural Networks Approach.J Voice. 2024 Jul;38(4):951-962. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2022.01.028. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J Voice. 2024. PMID: 35304042 Free PMC article.
-
Spasmodic dysphonia: let's look at that again.J Voice. 2014 Nov;28(6):694-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Voice. 2014. PMID: 24972536 Review.
-
Listening: the key to diagnosing spasmodic dysphonia.ORL Head Neck Nurs. 2008 Winter;26(1):8-12. ORL Head Neck Nurs. 2008. PMID: 18274236 Review.
Cited by
-
Supraglottic Laryngeal Maneuvers in Adductor Laryngeal Dystonia During Connected Speech.J Voice. 2024 Aug 30:S0892-1997(24)00257-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2024.08.009. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2024. PMID: 39217084
-
Vowel onset measures and their reliability, sensitivity and specificity: A systematic literature review.PLoS One. 2024 May 2;19(5):e0301786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301786. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38696537 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Analysis of Glottal Attack and Offset Times in Adductor Laryngeal Dystonia.J Voice. 2023 Nov 15:S0892-1997(23)00319-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.10.011. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2023. PMID: 37977969 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Glottal Attack Time and Glottal Offset Time in Neurogenic Voice Disorders During Sustained Phonation.J Voice. 2025 Mar 18:S0892-1997(25)00077-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2025.02.030. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 40107936
-
Investigation Methods for Vocal Onset-A Historical Perspective.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;11(10):989. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11100989. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DDeliyski D; Petrushev PP; Bonilha HS; Gerlach TT; Martin-Harris B; Hillman RE Clinical implementation of laryngeal high-speed videoendoscopy: Challenges and evolution. Folia Phoniatr. Et Logop 2008, 60, 33–44. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
