The phytase RipBL1 enables the assignment of a specific inositol phosphate isomer as a structural component of human kidney stones
- PMID: 37034402
- PMCID: PMC10074554
- DOI: 10.1039/d2cb00235c
The phytase RipBL1 enables the assignment of a specific inositol phosphate isomer as a structural component of human kidney stones
Abstract
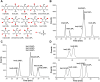
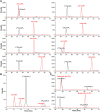
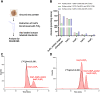
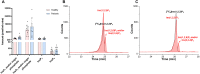
Inositol phosphates (InsPs) are ubiquitous in all eukaryotes. However, since there are 63 possible different phosphate ester isomers, the analysis of InsPs is challenging. In particular, InsP1, InsP2, and InsP3 already amass 41 different isomers, of which some occur as enantiomers. Profiling of these "lower" inositol phosphates in mammalian tissues requires powerful analytical methods and reference compounds. Here, we report an analysis of InsP2 and InsP3 with capillary electrophoresis coupled to electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (CE-ESI-MS). Using this method, the bacterial effector RipBL1 was analyzed and found to degrade InsP6 to Ins(1,2,3)P3, an understudied InsP3 isomer. This new reference molecule then aided us in the assignment of the isomeric identity of an InsP3 while profiling human samples: in urine and kidney stones, we describe for the first time the presence of defined and abundant InsP3 isomers, namely Ins(1,2,3)P3, Ins(1,2,6)P3 and/or Ins(2,3,4)P3.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Otto J. C. Kelly P. Chiou S. T. York J. D. Alterations in an inositol phosphate code through synergistic activation of a G protein and inositol phosphate kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007;104(40):15653–15658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705729104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705729104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dovey C. M. Diep J. Clarke B. P. Hale A. T. McNamara D. E. Guo H. Brown, Jr. N. W. Cao J. Y. Grace C. R. Gough P. J. Bertin J. Dixon S. J. Fiedler D. Mocarski E. S. Kaiser W. J. Moldoveanu T. York J. D. Carette J. E. MLKL Requires the Inositol Phosphate Code to Execute Necroptosis. Mol. Cell. 2018;70(5):936–948 e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.010. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ito M. Fujii N. Wittwer C. Sasaki A. Tanaka M. Bittner T. Jessen H. J. Saiardi A. Takizawa S. Nagata E. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the quantitative analysis of mammalian-derived inositol poly/pyrophosphates. J. Chromatogr. A. 2018;1573:87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2018.08.061. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2018.08.061. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

