A pilot randomized controlled trial of liraglutide 3.0 mg for binge eating disorder
- PMID: 37034559
- PMCID: PMC10073825
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.619
A pilot randomized controlled trial of liraglutide 3.0 mg for binge eating disorder
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy of liraglutide 3.0 mg, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, for binge eating disorder (BED).
Methods: Adults with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 27 kg/m2 enrolled in a pilot, 17-week double-blind, randomized controlled trial of liraglutide 3.0 mg/day for BED. The primary outcome was number of objective binge episodes (OBEs)/week. Binge remission, weight change, and psychosocial variables were secondary outcomes. Mixed effect models were used for continuous variables, and generalized estimating equations were used for remission rates.
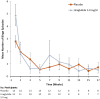
Results: Participants (n = 27) were 44.2 ± 10.6 years; BMI = 37.9 ± 11.8 kg/m2; 63% women; and 59% White and 41% Black. At baseline, the liraglutide group (n = 13) reported 4.7 ± 0.7 OBEs/week, compared with 3.0 ± 0.7 OBEs/week for the placebo group, p = 0.07. At week 17, OBEs/week decreased by 4.0 ± 0.6 in liraglutide participants and by 2.5 ± 0.5 in placebo participants (p = 0.37, mean difference = 1.2, 95% confidence interval 1.3, 2.0). BED remission rates of 44% and 36%, respectively, did not differ. Percent weight loss was significantly greater in the liraglutide versus the placebo group (5.2 ± 1.0% vs. 0.9 ± 0.7%, p = 0.005).
Conclusion: Participants in both groups reported reductions in OBEs, with the liraglutide group showing clinically meaningful weight loss. A pharmacy medication dispensing error was a significant limitation of this study. Further research on liraglutide and other GLP-1 agonists for BED is warranted.
Keywords: binge eating disorder; binge episodes; eating disorder; liraglutide; loss of control eating; weight loss medication.
© 2022 The Authors. Obesity Science & Practice published by World Obesity and The Obesity Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Ariana M. Chao reports grant funding from Eli Lilly and Company and WW International, Inc., outside the submitted work. Robert I. Berkowitz has received research grant support from Novo Nordisk and Eisai Inc. and has served as a scientific consultant to WW International. Thomas A. Wadden serves on scientific advisory boards for Novo Nordisk and WW International and has received grant support from Novo Nordisk and Epitomee Medical. Jena S. Tronieri has received consulting fees/honoraria from Novo Nordisk.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. 2013. 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources