This is a preprint.
Lysyl oxidase regulates epithelial differentiation and barrier integrity in eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 37034590
- PMCID: PMC10081173
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.03.27.534387
Lysyl oxidase regulates epithelial differentiation and barrier integrity in eosinophilic esophagitis
Update in
-
Lysyl Oxidase Regulates Epithelial Differentiation and Barrier Integrity in Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;17(6):923-937. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.01.025. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38340809 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background & aims: Epithelial disruption in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) encompasses both impaired differentiation and diminished barrier integrity. We have shown that lysyl oxidase (LOX), a collagen cross-linking enzyme, is upregulated in the esophageal epithelium in EoE. However, the functional roles of LOX in the esophageal epithelium remains unknown.
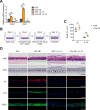
Methods: We investigated roles for LOX in the human esophageal epithelium using 3-dimensional organoid and air-liquid interface cultures stimulated with interleukin (IL)-13 to recapitulate the EoE inflammatory milieu, followed by single-cell RNA sequencing, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, western blot, histology, and functional analyses of barrier integrity.
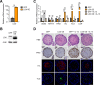
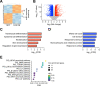
Results: Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis on patient-derived organoids revealed that LOX was induced by IL-13 in differentiated cells. LOX-overexpressing organoids demonstrated suppressed basal and upregulated differentiation markers. Additionally, LOX overexpression enhanced junctional protein genes and transepithelial electrical resistance. LOX overexpression restored the impaired differentiation and barrier function, including in the setting of IL-13 stimulation. Transcriptome analyses on LOX-overexpressing organoids identified enriched bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway compared to wild type organoids. Particularly, LOX overexpression increased BMP2 and decreased BMP antagonist follistatin. Finally, we found that BMP2 treatment restored the balance of basal and differentiated cells.
Conclusions: Our data support a model whereby LOX exhibits non-canonical roles as a signaling molecule important for epithelial homeostasis in the setting of inflammation via activation of BMP pathway in esophagus. The LOX/BMP axis may be integral in esophageal epithelial differentiation and a promising target for future therapies.
Keywords: BMP; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Lysyl oxidase; Organoid.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures Amanda B. Muir has served on the medical advisory boards for Nexstone Immunology and Bristol Meyers Squib. The rest of the authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Whelan KA, Godwin BC, Wilkins B, Elci OU, Benitez A, DeMarshall M, Sharma M, Gross J, Klein-Szanto AJ, Liacouras CA, Dellon ES, Spergel JM, Falk GW, Muir AB, Nakagawa H. Persistent Basal Cell Hyperplasia Is Associated With Clinical and Endoscopic Findings in Patients With Histologically Inactive Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2020;18:1475–82. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kasagi Y, Dods K, Wang JX, Chandramouleeswaran PM, Benitez AJ, Gambanga F, Kluger J, Ashorobi T, Gross J, Tobias JW, Klein-Szanto AJ, Spergel JM, Cianferoni A, Falk GW, Whelan KA, Nakagawa H, Muir AB. Fibrostenotic eosinophilic esophagitis might reflect epithelial lysyl oxidase induction by fibroblast-derived TNF-α. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2019;144:171–82. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Yang A, Jia J, Popov YV, Schuppan D, You H. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) Family Members: Rationale and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets for Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2020;72:729–41. - PubMed
-
- Mäki JM, Räsänen J, Tikkanen H, Sormunen R, Mäkikallio K, Kivirikko KI, Soininen R. Inactivation of the lysyl oxidase gene Lox leads to aortic aneurysms, cardiovascular dysfunction, and perinatal death in mice. Circulation 2002;106:2503–9. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
