This is a preprint.
A role for N6-methyldeoxyadenosine in C. elegans mitochondrial genome regulation
- PMID: 37034795
- PMCID: PMC10081187
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.03.27.534452
A role for N6-methyldeoxyadenosine in C. elegans mitochondrial genome regulation
Abstract
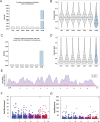
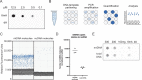
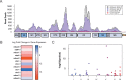
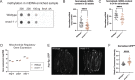
Epigenetic modifications provide powerful means for transmitting information from parent to progeny. As a maternally inherited genome that encodes essential components of the electron transport chain, the mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) is ideally positioned to serve as a conduit for the transgenerational transmission of metabolic information. Here, we provide evidence that mtDNA of C. elegans contains the epigenetic mark N6-methyldeoxyadenosine (6mA). Bioinformatic analysis of SMRT sequencing data and methylated DNA IP sequencing data reveal that C. elegans mtDNA is methylated at high levels in a site-specific manner. We further confirmed that mtDNA contains 6mA by leveraging highly specific anti-6mA antibodies. Additionally, we find that mtDNA methylation is dynamically regulated in response to antimycin, a mitochondrial stressor. Further, 6mA is increased in nmad-1 mutants and is accompanied by a significant decrease in mtDNA copy number. Our discovery paves the way for future studies to investigate the regulation and inheritance of mitochondrial epigenetics.
Keywords: 6mA; Mitochondria; epigenetics; mtDNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Fang G., Munera D., Friedman D.I., Mandlik A., Chao M.C., Banerjee O., Feng Z., Losic B., Mahajan M.C., Jabado O.J., et al. (2012). Genome-wide mapping of methylated adenine residues in pathogenic Escherichia coli using single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 30, 1232–1239. 10.1038/nbt.2432. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
