Activating a dormant metabolic pathway for high-temperature l-alanine production in Bacillus licheniformis
- PMID: 37034987
- PMCID: PMC10074574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106397
Activating a dormant metabolic pathway for high-temperature l-alanine production in Bacillus licheniformis
Abstract
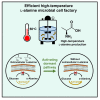
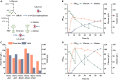
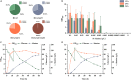
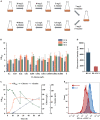
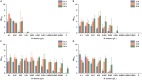
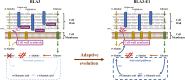
l-Alanine is an important amino acid widely used in food, medicine, materials, and other fields. Here, we develop Bacillus licheniformis as an efficient l-alanine microbial cell factory capable of realizing high-temperature fermentation. By enhancing the glycolytic pathway, knocking out the by-product pathways and overexpressing the thermostable alanine dehydrogenase, the engineered B. licheniformis strain BLA3 produced 93.7 g/L optically pure l-alanine at 50°C. Subsequently, d-alanine dependence of an alanine racemase-deficient strain is relieved by adaptive laboratory evolution, implying that a dormant alternative pathway for d-alanine synthesis is activated in the evolved strain. The d-amino acid aminotransferase Dat1 is shown to be a key enzyme in the dormant alternative pathway. Molecular mechanism of the d-alanine dependence is revealed via mutational analysis. This study demonstrates a novel technology for high-temperature l-alanine production and shows that activating dormant metabolic pathway(s) is an effective strategy of metabolic engineering.
Keywords: Applied microbiology; Microbial biotechnology; Microbiology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li T., Cui X., Cui Y., Sun J., Chen Y., Zhu T., Li C., Li R., Wu B. Exploration of transaminase diversity for the oxidative conversion of natural amino acids into 2-ketoacids and high-value chemicals. ACS Catal. 2020;10:7950–7957. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c01895. - DOI
-
- Porcellati F., Pampanelli S., Rossetti P., Busciantella Ricci N., Marzotti S., Lucidi P., Santeusanio F., Bolli G.B., Fanelli C.G. Effect of the amino acid alanine on glucagon secretion in non-diabetic and type 1 diabetic subjects during hyperinsulinaemic euglycaemia, hypoglycaemia and post-hypoglycaemic hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia. 2007;50:422–430. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0519-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

