A genetically targeted ion sensor reveals distinct seizure-related chloride and pH dynamics in GABAergic interneuron populations
- PMID: 37034992
- PMCID: PMC10074576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106363
A genetically targeted ion sensor reveals distinct seizure-related chloride and pH dynamics in GABAergic interneuron populations
Abstract
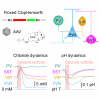
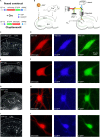
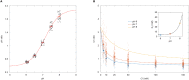
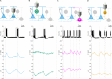
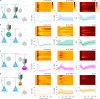
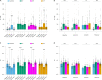
Intracellular chloride and pH play fundamental roles in determining a neuron's synaptic inhibition and excitability. Yet it has been difficult to measure changes in these ions during periods of heightened network activity, such as occur in epilepsy. Here we develop a version of the fluorescent reporter, ClopHensorN, to enable simultaneous quantification of chloride and pH in genetically defined neurons during epileptiform activity. We compare pyramidal neurons to the major GABAergic interneuron subtypes in the mouse hippocampus, which express parvalbumin (PV), somatostatin (SST), or vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Interneuron populations exhibit higher baseline chloride, with PV interneurons exhibiting the highest levels. During an epileptiform discharge, however, all subtypes converge upon a common elevated chloride level. Concurrent with these dynamics, epileptiform activity leads to different degrees of intracellular acidification, which reflect baseline pH. Thus, a new optical tool for dissociating chloride and pH reveals neuron-specific ion dynamics during heightened network activity.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Molecular neuroscience; Neuroscience; Techniques in neuroscience.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. The manuscript was approved by all of the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Staley K.J., Soldo B.L., Proctor W.R. Ionic mechanisms of neuronal excitation by inhibitory GABAA receptors. Science. 1995;269:977–981. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

