Marine-derived biopolymers as potential bioplastics, an eco-friendly alternative
- PMID: 37034997
- PMCID: PMC10074575
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106404
Marine-derived biopolymers as potential bioplastics, an eco-friendly alternative
Abstract
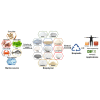
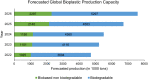
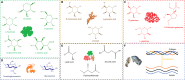
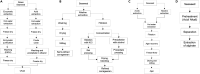
The manufacturing and consumption of plastic products have steadily increased over the past decades due to rising global demand, resulting not only in the depletion of petroleum resources but also increased environmental pollution due to the non-biodegradable nature of conventional plastics. Moreover, despite being introduced into the market as an alternative to conventional petroleum-based plastics, biobased plastics are mainly manufactured from agricultural crop-based sources, which has negative impacts on the environment and the livelihoods of people. Marine-derived bioplastics are becoming a promising and cost-effective solution to the rising demand for plastic products. The physicochemical, biological, and degradation properties of marine-derived bioplastics have made them promising substances for many applications. However, more research is required for their large-scale implementation. Therefore, this review summarizes the raw materials of marine-derived bioplastics such as algae, animals, and microorganisms, as well as their extraction processes and properties. These insights could thus accelerate the production of marine-derived bioplastics as a novel alternative to prevailing bioplastics by taking advantage of marine biomass.
Keywords: Aquatic science; Natural resources; Oceanography.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this review paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The degradation of single-use plastics and commercially viable bioplastics in the environment: A review.Environ Res. 2023 Aug 15;231(Pt 1):115988. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115988. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37105296 Review.
-
Organic waste-to-bioplastics: Conversion with eco-friendly technologies and approaches for sustainable environment.Environ Res. 2024 Mar 1;244:117949. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117949. Epub 2023 Dec 17. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38109961 Review.
-
Recent developments in non-biodegradable biopolymers: Precursors, production processes, and future perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jan;103(1):143-157. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9483-6. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30397765 Review.
-
Bioplastics from waste biomass of marine and poultry industries.J Biosci. 2023;48:11. J Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37021675 Review.
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoates, the bioplastics of microbial origin: Properties, biochemical synthesis, and their applications.Chemosphere. 2022 May;294:133723. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133723. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35085614 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Characterization of Polymeric-based Biomaterial from Agro-food Waste: A Sustainable and Eco-friendly Approach Towards Plastic Pollution.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(4):550-563. doi: 10.2174/0113892010304507240528064315. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38847261
-
Surface modification strategies for improved hemocompatibility of polymeric materials: a comprehensive review.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 1;14(11):7440-7458. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08738g. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38433935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injectable Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels: A Next-Generation Platform for Minimally Invasive Therapeutics.Gels. 2025 May 23;11(6):383. doi: 10.3390/gels11060383. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40558682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valorization of Algal Biomass to Produce Microbial Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Recent Updates, Challenges, and Perspectives.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;16(15):2227. doi: 10.3390/polym16152227. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction of Natural-Based Raw Materials Towards the Production of Sustainable Man-Made Organic Fibres.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Dec 23;16(24):3602. doi: 10.3390/polym16243602. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sankhla I.S., Sharma G., Tak A. Fungal degradation of bioplastics: an overview. New Futur. Dev. Microb. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020:35–47. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-821007-9.00004-8. - DOI
-
- Devi R.S., Kannan V.R., Natarajan K., Nivas D., Kannan K., Chandru S., Antony A.R. In: Environmental Waste Management. Chandra R., editor. CRC Press; 2016. The role of microbes in plastic degradation; pp. 341–370. - DOI
-
- Global Plastics Industry - Statistics & Facts | Statista. https://www.statista.com/topics/5266/plastics-industry/#dossierKeyfigures.
-
- Gadhave R.V., Das A., Mahanwar P.A., Gadekar P.T. Starch based bio-plastics: the future of sustainable packaging. OJPChem. 2018;08:21–33. doi: 10.4236/ojpchem.2018.82003. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

