Phyto-assisted synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for developing antibiofilm surface coatings on central venous catheters
- PMID: 37035110
- PMCID: PMC10076889
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1138333
Phyto-assisted synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for developing antibiofilm surface coatings on central venous catheters
Abstract
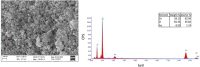
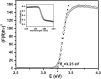
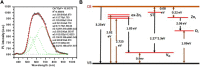
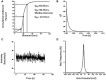
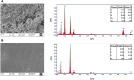
Medical devices such as Central Venous Catheters (CVCs), are routinely used in intensive and critical care settings. In the present scenario, incidences of Catheter-Related Blood Stream Infections (CRBSIs) pose a serious challenge. Despite considerable advancements in the antimicrobial therapy and material design of CVCs, clinicians continue to struggle with infection-related complications. These complications are often due colonization of bacteria on the surface of the medical devices, termed as biofilms, leading to infections. Biofilm formation is recognized as a critical virulence trait rendering infections chronic and difficult to treat even with 1,000x, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics. Therefore, non-antibiotic-based solutions that prevent bacterial adhesion on medical devices are warranted. In our study, we report a novel and simple method to synthesize zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using ethanolic plant extracts of Eupatorium odoratum. We investigated its physio-chemical characteristics using Field Emission- Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy dispersive X-Ray analysis, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Photoluminescence Spectroscopy, UV-Visible and Diffuse Reflectance spectroscopy, and Dynamic Light Scattering characterization methods. Hexagonal phase with wurtzite structure was confirmed using XRD with particle size of ∼50 nm. ZnO nanoparticles showed a band gap 3.25 eV. Photoluminescence spectra showed prominent peak corresponding to defects formed in the synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. Clinically relevant bacterial strains, viz., Proteus aeruginosa PAO1, Escherichia coli MTCC 119 and Staphylococcus aureus MTCC 7443 were treated with different concentrations of ZnO NPs. A concentration dependent increase in killing efficacy was observed with 99.99% killing at 500 μg/mL. Further, we coated the commercial CVCs using green synthesized ZnO NPs and evaluated it is in vitro antibiofilm efficacy using previously optimized in situ continuous flow model. The hydrophilic functionalized interface of CVC prevents biofilm formation by P. aeruginosa, E. coli and S. aureus. Based on our findings, we propose ZnO nanoparticles as a promising non-antibiotic-based preventive solutions to reduce the risk of central venous catheter-associated infections.
Keywords: anti-biofilm coatings; anti-microbial resistance; device associated infections; green synthesis; medical devices; nanoparticle coatings; plant mediated synthesis; zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs).
Copyright © 2023 Malhotra, Chauhan, Rahaman, Tripathi, Khanuja and Chauhan.
Conflict of interest statement
AM is Co-Founder, Invisiobiome Pvt. Ltd., India. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Antonelli M., de Pascale G., Ranieri V. M., Pelaia P., Tufano R., Piazza O., et al. (2012). Comparison of triple-lumen central venous catheters impregnated with silver nanoparticles (AgTive®) vs conventional catheters in intensive care unit patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 82 (2), 101–107. 10.1016/j.jhin.2012.07.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Björling G., Johansson D., Bergström L., Strekalovsky A., Sanchez J., Frostell C., et al. (2018). Evaluation of central venous catheters coated with a noble metal alloy—a randomized clinical pilot study of coating durability, performance and tolerability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 106 (6), 2337–2344. 10.1002/jbm.b.34041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

