Analysis of risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma and establishment of a clinical prognosis model
- PMID: 37035138
- PMCID: PMC10073455
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1067353
Analysis of risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma and establishment of a clinical prognosis model
Abstract
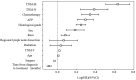
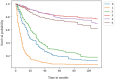
Liver cancer is a common malignancy of the digestive system. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for the most majority of these tumors and it has brought a heavy medical burden to underdeveloped countries and regions. Many factors affect the prognosis of HCC patients, however, there is no specific statistical model to predict the survival time of clinical patients. This study derived a risk factor signature of HCC and reliable clinical prediction model by statistically analyzing The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database patient information using an open source package in the python environment.
Keywords: HCC (hepatic cellular carcinoma); SEER (Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results) database; machine learning - ML; random survival forest model; risk factors.
Copyright © 2023 Ge, Sun, Wang, Wang, Liu, Yang, Lu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-term prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with lung metastasis: A retrospective cohort study based on the SEER database.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 11;101(45):e31399. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031399. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36397445 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Personalized surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis - using machine learning adapted to HCV status.J Hepatol. 2020 Dec;73(6):1434-1445. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.052. Epub 2020 Jun 29. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32615276
-
Identifying hepatocellular carcinoma patients with survival benefits from surgery combined with chemotherapy: based on machine learning model.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Dec 1;20(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02837-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36451200 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathologic features, treatment, survival, and prognostic factors of combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma: A nomogram development based on SEER database and validation in multicenter study.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jul;48(7):1559-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2022.01.023. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35115213
-
Survival improvement and prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the SEER database.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 29;21(1):1157. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08904-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34715816 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dynamic conditional survival nomogram for primary hepatocellular carcinoma: a population-based analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 21;16(1):854. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02642-9. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40399541 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of surgery on overall survival and cancer-specific survival in patients with primary HCC: A study based on PSM in the SEER cohort.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 21;104(8):e41521. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041521. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39993067 Free PMC article.
-
Rare Coexisting Hepatocellular and Gallbladder Carcinomas: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2025 May 7;26:e946739. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.946739. Am J Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40333567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbate V, Marcantoni M, Giuliante F, Vecchio FM, Gatto I, Mele C, et al. . Heppar1-positive circulating microparticles are increased in subjects with hepatocellular carcinoma and predict early recurrence after liver resection. Int J Mol Sci (2017) 18(5). doi: 10.3390/ijms18051043 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources