Glucocorticoid mediated inhibition of LKB1 mutant non-small cell lung cancers
- PMID: 37035141
- PMCID: PMC10078807
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1025443
Glucocorticoid mediated inhibition of LKB1 mutant non-small cell lung cancers
Abstract
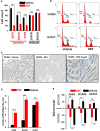
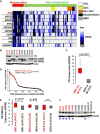
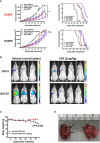
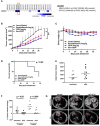
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is an important anti-cancer target in lymphoid cancers but has been understudied in solid tumors like lung cancer, although glucocorticoids are often given with chemotherapy regimens to mitigate side effects. Here, we identify a dexamethasone-GR mediated anti-cancer response in a subset of aggressive non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) that harbor Serine/Threonine Kinase 11 (STK11/LKB1) mutations. High tumor expression of carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1) was strongly linked to the presence of LKB1 mutations, was the best predictor of NSCLC dexamethasone (DEX) sensitivity (p < 10-16) but was not mechanistically involved in DEX sensitivity. Subcutaneous, orthotopic and metastatic NSCLC xenografts, biomarker-selected, STK11/LKB1 mutant patient derived xenografts, and genetically engineered mouse models with KRAS/LKB1 mutant lung adenocarcinomas all showed marked in vivo anti-tumor responses with the glucocorticoid dexamethasone as a single agent or in combination with cisplatin. Mechanistically, GR activation triggers G1/S cell cycle arrest in LKB1 mutant NSCLCs by inducing the expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, CDKN1C/p57(Kip2). All findings were confirmed with functional genomic experiments including CRISPR knockouts and exogenous expression. Importantly, DEX-GR mediated cell cycle arrest did not interfere with NSCLC radiotherapy, or platinum response in vitro or with platinum response in vivo. While DEX induced LKB1 mutant NSCLCs in vitro exhibit markers of cellular senescence and demonstrate impaired migration, in vivo DEX treatment of a patient derived xenograft (PDX) STK11/LKB1 mutant model resulted in expression of apoptosis markers. These findings identify a previously unknown GR mediated therapeutic vulnerability in STK11/LKB1 mutant NSCLCs caused by induction of p57(Kip2) expression with both STK11 mutation and high expression of CPS1 as precision medicine biomarkers of this vulnerability.
Keywords: LKB1; glucocorticoid; lung cancer; nuclear receptor; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Huffman, Li, Carstens, Park, Girard, Avila, Wei, Kollipara, Timmons, Sudderth, Bendris, Kim, Villalobos, Fujimoto, Schmid, Deberardinis, Wistuba, Heymach, Kittler, Akbay, Posner, Wang, Lam, Kliewer, Mangelsdorf and Minna.
Conflict of interest statement
JM supported by P50 CA070907, U54 CA224065, CA142543, CPRIT RP120732. DM supported by HHMI Investigators Program. RD supported by R35 CA22044901 and HHMI Investigators Program. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AXL targeting restores PD-1 blockade sensitivity of STK11/LKB1 mutant NSCLC through expansion of TCF1+ CD8 T cells.Cell Rep Med. 2022 Mar 15;3(3):100554. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100554. eCollection 2022 Mar 15. Cell Rep Med. 2022. PMID: 35492873 Free PMC article.
-
Caloric restriction and metformin selectively improved LKB1-mutated NSCLC tumor response to chemo- and chemo-immunotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 2;43(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02933-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38163906 Free PMC article.
-
WEE1 Kinase Inhibitor AZD1775 Has Preclinical Efficacy in LKB1-Deficient Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;77(17):4663-4672. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3565. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28652249
-
Unraveling the Role of STK11/LKB1 in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Cureus. 2022 Jan 10;14(1):e21078. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21078. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35165542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LKB1: Can We Target an Hidden Target? Focus on NSCLC.Front Oncol. 2022 May 11;12:889826. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889826. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35646638 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling in NSCLC: Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Perspectives.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 23;13(9):1286. doi: 10.3390/biom13091286. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759686 Free PMC article.
-
Screening biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1 overexpression.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(14):12965-12976. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05160-9. Epub 2023 Jul 19. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37468609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez-Cespedes M, Parrella P, Esteller M, Nomoto S, Trink B, Engles JM, et al. . Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event in adenocarcinomas of the lung. Cancer Res (2002) 62(13):3659–62. - PubMed
-
- Skoulidis F, Byers LA, Diao L, Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Tong P, Izzo J, et al. . Co-Occurring genomic alterations define major subsets of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma with distinct biology, immune profiles, and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Discovery (2015) 5(8):860–77. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1236 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

