Clinical efficacy of laparoscopic radical hepatectomy and laparotomy for hepatocellular carcinoma and factors of postoperative recurrence
- PMID: 37035189
- PMCID: PMC10073724
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1116984
Clinical efficacy of laparoscopic radical hepatectomy and laparotomy for hepatocellular carcinoma and factors of postoperative recurrence
Abstract
Objective: For exploring the clinical efficacy of laparoscopic radical hepatectomy and laparotomy for hepatocellular carcinoma and analysing related factors of postoperative recurrence.
Methods: Totally 212 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma admitted to our hospital between April 2017 and December 2020 were enrolled, and all of them were followed up after the operation. According to the treatment modes, the patients were assigned to a laparotomy group (n=106) and a laparoscopic group (n=106). Perioperative indicators, haematological examination results, complications and recurrence were compared between the two groups. The recurrence time of hepatocellular carcinoma after the operation was confirmed by imaging examination with definite mass, and logistic multivariate analysis was used for analyzing the risk factors associated with postoperative recurrence.
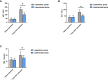
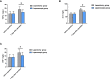
Results: Patients in both groups were comparable in terms of general baseline data. The laparoscopic group experienced longer operation time and shorter incision length, less intraoperative blood loss, early time to have the first off-bed activity and time to eat liquid and shorter hospital stay than the laparotomy group (all P<0.05). Seven days after the operation, the laparoscopic group showed notably lower levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-8 (IL-8), and C-reactive protein (CRP) than the laparotomy group (all P<0.05), and also showed notably higher levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA), IgG and IgM than the laparotomy group (all P<0.05). Additionally, the laparotomy group showed a higher total incidence rate of complications than the laparoscopic group (19.81% vs. 9.43%, P<0.05). During the one-year follow-up, the laparotomy group was not greatly different from the laparoscopic group in recurrence rate (22.64% (24/106) vs. 16.98% (18/106), P>0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that average tumour diameter and microvascular invasion were risk factors for postoperative recurrence (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Laparoscopic radical hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma can reduce the influence on liver function and immune function, with less damage to tissues, and can ameliorate postoperative inflammatory reaction, and promote postoperative recovery of patients as soon as possible. There are many factors influencing the postoperative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma, and average tumour diameter and microvascular invasion are the risk factors.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; high risk factors; laparoscopic radical hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma; laparotomy; recurrence.
Copyright © 2023 Cao, Yang, Zhou and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparative study of laparoscopic precise hepatectomy with conventional open hepatectomy in the treatment of primary hepatocellular cancer.J BUON. 2019 Sep-Oct;24(5):1943-1949. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31786859
-
Prospective, single-center cohort study analyzing the efficacy of complete laparoscopic resection on recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Mar 8;35:25. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0088-0. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26956022 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function after laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):8156-8165. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505328 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and feasibility of laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in the posterosuperior liver segments.World J Surg. 2015 May;39(5):1202-9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-2946-3. World J Surg. 2015. PMID: 25585525
-
Retroperitoneal laparoscopic hepatectomy of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: case report and literature review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug 20;20(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01380-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32819277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between anesthesia, surgery and postoperative immune function in cancer patients: a review.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1441020. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1441020. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

