Effectiveness of 7-day triple therapy with half-dose clarithromycin for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori without the A2143G and A2142G point mutations of the 23S rRNA gene in a high clarithromycin resistance area
- PMID: 37035320
- PMCID: PMC10073449
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1150396
Effectiveness of 7-day triple therapy with half-dose clarithromycin for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori without the A2143G and A2142G point mutations of the 23S rRNA gene in a high clarithromycin resistance area
Abstract
Background: Tailored therapy has been widely used for patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in South Korea. Herein, we evaluated the treatment outcomes of tailored clarithromycin-based triple therapy (TT) in patients infected with H. pylori.
Methods: We enrolled 460 patients without A2142G and A2143G point mutations by dual priming oligonucleotide-based polymerase chain reaction who had taken TT and undergone the urease breath test to evaluate eradication in clinical practice. Eradication rates according to the treatment duration and dose of clarithromycin were analyzed.
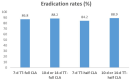
Results: Among 460 patients (164 women, median age 63.0 years), 250 patients underwent TT with full-dose clarithromycin (TT-full CLA), and 216 patients underwent TT with half-dose clarithromycin (TT-half CLA). The eradication rates were 88.0% (220/250) in patients with TT-full CLA and 85.2% (179/210) in patients with TT-half CLA. In 250 patients with TT-full CLA, the eradication rates were 86.8% (33/38) in patients with 7-day TT-full CLA and 88.2% (187/212) in patients with 10-day or 14-day TT-full CLA (P = 0.788). In 210 patients with TT-half CLA, the eradication rates were 84.2% (139/165) in those with a 7-day TT-half CLA and 88.9% (40/45) in those with a 10-day or 14-day TT-half CLA (P = 0.436).
Conclusion: For patients with H. pylori infection without A2142G and A2143G point mutations by DPO-PCR in clinical practice, treatment extension above 7-day TT with full CLA did not improve the eradication rates. Future studies on the treatment outcomes of TT-half CLA considering effectiveness and compliance are warranted.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; clarithromycin; eradication; point mutation; resistance.
Copyright © 2023 Cho, Park, Park, Kim, You and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

