An Artificial Intelligence Training Workshop for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
- PMID: 37035436
- PMCID: PMC10077074
- DOI: 10.1148/ryai.220170
An Artificial Intelligence Training Workshop for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
Abstract
Purpose: To develop, implement, and evaluate feedback for an artificial intelligence (AI) workshop for radiology residents that has been designed as a condensed introduction of AI fundamentals suitable for integration into an existing residency curriculum.
Materials and methods: A 3-week AI workshop was designed by radiology faculty, residents, and AI engineers. The workshop was integrated into curricular academic half-days of a competency-based medical education radiology training program. The workshop consisted of live didactic lectures, literature case studies, and programming examples for consolidation. Learning objectives and content were developed for foundational literacy rather than technical proficiency. Identical prospective surveys were conducted before and after the workshop to gauge the participants' confidence in understanding AI concepts on a five-point Likert scale. Results were analyzed with descriptive statistics and Wilcoxon rank sum tests to evaluate differences.
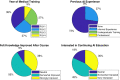
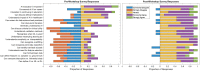
Results: Twelve residents participated in the workshop, with 11 completing the survey. An average score of 4.0 ± 0.7 (SD), indicating agreement, was observed when asking residents if the workshop improved AI knowledge. Confidence in understanding AI concepts increased following the workshop for 16 of 18 (89%) comprehension questions (P value range: .001 to .04 for questions with increased confidence).
Conclusion: An introductory AI workshop was developed and delivered to radiology residents. The workshop provided a condensed introduction to foundational AI concepts, developed positive perception, and improved confidence in AI topics.Keywords: Medical Education, Machine Learning, Postgraduate Training, Competency-based Medical Education, Medical Informatics Supplemental material is available for this article. © RSNA, 2023.
Keywords: Competency-based Medical Education; Machine Learning; Medical Education; Medical Informatics; Postgraduate Training.
© 2023 by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of conflicts of interest: R.H. No relevant relationships. A.R. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence trainee editorial board member. Z.H. No relevant relationships. T.L. Unpaid volunteer director for LEADs Employment Services Board of Directors. A.D.C. No relevant relationships. B.Y.M.K. Queen’s University Department of Radiology Research Grant.
Figures


References
-
- Kulkarni S , Seneviratne N , Baig MS , Khan AHA . Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: Where Are We Now? Acad Radiol 2020. ; 27 ( 1 ): 62 – 70 . - PubMed
-
- Wood MJ , Tenenholtz NA , Geis JR , Michalski MH , Andriole KP . The Need for a Machine Learning Curriculum for Radiologists . J Am Coll Radiol 2019. ; 16 ( 5 ): 740 – 742 . - PubMed
-
- Collado-Mesa F , Alvarez E , Arheart K . The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Radiology: A Survey at a Single Radiology Residency Training Program . J Am Coll Radiol 2018. ; 15 ( 12 ): 1753 – 1757 . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

