Role of IP-10 to Predict Clinical Progression and Response to IL-6 Blockade With Sarilumab in Early COVID-19 Pneumonia. A Subanalysis of the SARICOR Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37035487
- PMCID: PMC10077828
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofad133
Role of IP-10 to Predict Clinical Progression and Response to IL-6 Blockade With Sarilumab in Early COVID-19 Pneumonia. A Subanalysis of the SARICOR Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: The Clinical Trial of Sarilumab in Adults With COVID-19 (SARICOR) showed that patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia and increased levels of interleukin (IL)-6 might benefit from blockade of the IL-6 pathway. However, the benefit from this intervention might not be uniform. In this subanalysis, we sought to determine if other immunoactivation markers, besides IL-6, could identify which subgroup of patients benefit most from this intervention.
Methods: The SARICOR trial was a phase II, open-label, multicenter, controlled trial (July 2020-March 2021) in which patients were randomized to receive usual care (UC; control group), UC plus a single dose of sarilumab 200 mg (sarilumab-200 group), or UC plus a single dose of sarilumab 400 mg (sarilumab-400 group). Patients who had baseline serum samples for cytokine determination (IL-8, IL-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, interferon-inducible protein [IP]-10) were included in this secondary analysis. Progression to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) according to cytokine levels and treatment received was evaluated.
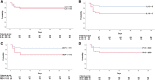
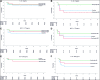
Results: One hundred one (88%) of 115 patients enrolled in the SARICOR trial had serum samples (control group: n = 33; sarilumab-200: n = 33; sarilumab-400: n = 35). Among all evaluated biomarkers, IP-10 showed the strongest association with treatment outcome. Patients with IP-10 ≥2500 pg/mL treated with sarilumab-400 had a lower probability of progression (13%) compared with the control group (58%; hazard ratio, 0.19; 95% CI, 0.04-0.90; P = .04). Conversely, patients with IP-10 <2500 pg/mL did not show these differences.
Conclusions: IP-10 may predict progression to ARDS in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and IL-6 levels >40 pg/mL. Importantly, IP-10 value <2500 pg/mL might discriminate those individuals who might not benefit from sarilumab therapy among those with high IL-6 levels.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; IP-10; SARS-CoV-2; sarilumab; tocilizumab.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest. All authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

