Identification of feature genes and key biological pathways in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy: High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 37035552
- PMCID: PMC10074409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.019
Identification of feature genes and key biological pathways in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy: High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), a subgroup of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs), is characterized by severe proximal muscle weakness and prominent necrotic fibers but no infiltration of inflammatory cells. IMNM pathogenesis is unclear. This study investigated key biomarkers and potential pathways for IMNM using high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics technology.
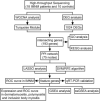
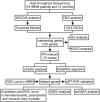
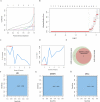
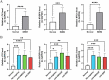
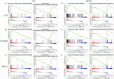
Methods: RNA sequencing was conducted in 18 IMNM patients and 10 controls. A combination of weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) and differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis was conducted to identify IMNM-related DEGs. Feature genes were screened out by employing the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, support vector machine-recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE), and least absolute shrinkage selection operator (LASSO). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to verify their differential expression, and the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to evaluate their diagnostic efficiency. Functional enrichment analysis was applied to reveal the hidden functions of feature genes. Furthermore, 28 immune cell abundance patterns in IMNM samples were measured.
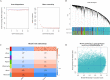
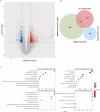
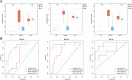
Results: We identified 193 IMNM-related DEGs that were aberrantly upregulated in the IMNM population and were closely associated with immune-inflammatory responses, regulation of skeletal and cardiac muscle contraction, and lipoprotein metabolism. With the help of the PPI network and the LASSO and SVM-RFE algorithms, three feature genes, LTK, MYBPH, and MYL4, were identified and further confirmed by qRT-PCR. ROC curves among IMNM, dermatomyositis (DM), inclusion body myositis (IBM), and polymyositis (PM) samples validated the LTK and MYL4 genes as IMNM-specific feature markers. In addition, all three genes had a notable association with the autophagy-lysosome pathway and immune-inflammatory responses. Ultimately, IMNM displayed a marked immune-cell infiltrative microenvironment. The most significant correlation was found between CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells (DCs).
Conclusions: LTK, MYBPH, and MYL4 were identified as potential key molecules for IMNM and are believed to play a role in the autophagy-lysosome pathway and muscle inflammation.
Keywords: Autophay-lysosome pathway; Biomarkers; IMNM; Immune cell infiltration; RNA sequencing.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Li Zeng reports article publishing charges was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China. Qiao Zhou reports writing assistance was provided by Sichuan Science and Technology Bureau. Li Zeng reports a relationship with Chengdu Digidite Group Company that includes: non-financial support.
Figures


References
-
- Hoogendijk J.E., Amato A.A., Lecky B.R., Choy E.H., Lundberg I.E., Rose M.R., et al. 119th Enmc international workshop: trial design in adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, with the exception of inclusion body myositis, 10–12 october 2003, Naarden, the Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord. 2004;14(5):337–345. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2004.02.006. [Epub 2004/04/22] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lim J., Rietveld A., De Bleecker J.L., Badrising U.A., Saris C.G.J., van der Kooi A.J., et al. Seronegative patients form a distinctive subgroup of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2019;6(1) doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000513. [Epub 2018/10/23] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
