Combined Therapy with Laser and Autologous Topical Serum for Facial Rejuvenation: A Multiple Case Series Report
- PMID: 37035594
- PMCID: PMC10081471
- DOI: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_159_21
Combined Therapy with Laser and Autologous Topical Serum for Facial Rejuvenation: A Multiple Case Series Report
Abstract
Background: Lasers require several sessions to achieve significant results and may lead to adverse reactions. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a good adjuvant to laser therapies; however, repeated blood extractions and invasive injections are needed. A 100% autologous topical formulation based on the patient's proteins has been recently developed, known as Endoret-Serum (ES). Unlike other PRPs, ES provides a home care, storable, and topical needle-free application.
Objective: Preliminarily assess the clinical performance of a single session of the combined therapy with nonablative laser and ES in the management of cutaneous pigmented and vasculature lesions.
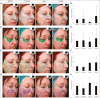
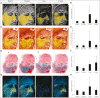
Materials and methods: Nine patients with clinical signs of skin aging received a single session of nonablative laser. ES was topically applied twice daily. They were clinically assessed after 1 and 8 weeks. VISIA-CR System was used for high-resolution topographic analysis. Subjects were asked to complete a self-assessment questionnaire and an impression of improvement survey. An investigator's global assessment scale was fulfilled.
Results: The combined treatment improved cutaneous spots, wrinkles, and texture after 8 weeks, whereas significant pore reduction was observable at 1 week. Ultraviolet (UV) spots and porphyrins decreased at 1 week, whereas red area improvement was noticeable after 8 weeks. Overall wrinkle amelioration, periorbital hyperpigmentation decrease, softened skin, and tone recovery was observed. Patients referred to be very satisfied and felt that their cutaneous condition was much better. At the end of the study, subjects presented minimal dermatological symptoms like pigmented lesions, redness, or capillaries. No side effects were reported.
Conclusion: Results presented herein suggest that one session of laser in combination with ES provides a good clinical outcome.
Keywords: Autologous topical serum; laser; platelet-rich plasma; skin rejuvenation.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined therapy with Endoret-Gel and plasma rich in growth factors vs Endoret-Gel alone in the management of facial rejuvenation: A comparative study.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Oct;19(10):2616-2626. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13661. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32757356
-
A Single-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of the Effectiveness of ANT1 Soybean Extract Cream on Skin Recovery After Nd: YAG Laser Treatment.Ann Plast Surg. 2018 Feb;80(2S Suppl 1):S26-S29. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001287. Ann Plast Surg. 2018. PMID: 29369914 Clinical Trial.
-
Erbium fractional laser irradiation combined with autologous platelet-rich plasma and platelet-poor plasma application for facial rejuvenation.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Aug;19(8):1975-1979. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13241. Epub 2019 Dec 13. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31833646
-
Rejuvenating the periorbital area using platelet-rich plasma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2021 Nov;313(9):711-727. doi: 10.1007/s00403-020-02173-z. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021. PMID: 33433716
-
A systematic review of the safety and effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for skin aging.Arch Dermatol Res. 2020 Jul;312(5):301-315. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-01999-6. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Arch Dermatol Res. 2020. PMID: 31628542
Cited by
-
Autolougous platelet concentrates in esthetic medicine.Periodontol 2000. 2025 Feb;97(1):363-419. doi: 10.1111/prd.12582. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Periodontol 2000. 2025. PMID: 39086171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe S. Basics of laser application to dermatology. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008;300:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Manstein D, Herron GS, Sink RK, Tanner H, Anderson RR. Fractional photothermolysis: A new concept for cutaneous remodeling using microscopic patterns of thermal injury. Lasers Surg Med. 2004;34:426–38. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RR. Lasers in dermatology–a critical update. J Dermatol. 2000;27:700–5. - PubMed
-
- Fisher GH, Geronemus RG. Short-term side effects of fractional photothermolysis. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:1245–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
