Genomic profiling of WRKY transcription factors and functional analysis of CcWRKY7, CcWRKY29, and CcWRKY32 related to protoberberine alkaloids biosynthesis in Coptis chinensis Franch
- PMID: 37035743
- PMCID: PMC10076542
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1151645
Genomic profiling of WRKY transcription factors and functional analysis of CcWRKY7, CcWRKY29, and CcWRKY32 related to protoberberine alkaloids biosynthesis in Coptis chinensis Franch
Abstract
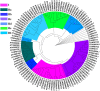
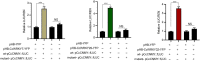
Coptis chinensis Franch. (Huanglian in Chinese) is an important economic crop with medicinal value. Its rhizome has been used as a traditional herbal medicine for thousands of years in Asia. Protoberberine alkaloids, as the main bioactive component of Coptis chinensis, have a series of pharmacological activities. However, the protoberberine alkaloids content of C. chinensis is relatively low. Understanding the molecular mechanisms affecting the transcriptional regulation of protoberberine alkaloids would be crucial to increase their production via metabolic engineering. WRKY, one of the largest plant-specific gene families, regulates plant defense responses via the biosynthesis of specialized metabolites such as alkaloids. Totally, 41 WRKY transcription factors (TFs) related to protoberberine alkaloid biosynthesis were identified in the C. chinensis genome and classified into three groups based on phylogenetic and conserved motif analyses. Three WRKY genes (CcWRKY7, CcWRKY29, and CcWRKY32) may regulate protoberberine alkaloid biosynthesis, as suggested by gene-specific expression patterns, metabolic pathways, phylogenetic, and dual-luciferase analysis. Furthermore, the CcWRKY7, CcWRKY29, and CcWRKY32 proteins were specifically detected in the nucleus via subcellular localization. This study provides a basis for understanding the regulatory mechanisms of protoberberine alkaloid biosynthesis and valuable information for breeding C. chinensis varieties.
Keywords: Coptis chinensis; WRKY family; berberine biosynthesis; protoberberine alkaloids; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Jia, Huang, Wang, Yang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coptis Chinensis Franch: Substance Basis, Mechanism of Action and Quality Control Standard Revealed Based on the Q-marker Concept and New Strategy of Systemic Pharmacology and Biosynthesis Research.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(23):2013-2032. doi: 10.2174/0115680266305274240723120426. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39136504 Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis of bHLH gene family in Coptis chinensis provides insights into the regulatory role in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023 Aug;201:107846. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107846. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37390693
-
Analysis of the Coptis chinensis genome reveals the diversification of protoberberine-type alkaloids.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 2;12(1):3276. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23611-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34078898 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals cadmium exposure enhanced the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis and disease resistance in Coptis chinensis.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Feb;271:115940. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.115940. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38218103
-
[Research progress on medicinal resources of Coptis and its isoquinoline alkaloids].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jul;46(14):3504-3513. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210430.103. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34402272 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in Sophora flavescens during tissue development and salt stress.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Dec 23;15:1520786. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1520786. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39764231 Free PMC article.
-
Coptis Chinensis Franch: Substance Basis, Mechanism of Action and Quality Control Standard Revealed Based on the Q-marker Concept and New Strategy of Systemic Pharmacology and Biosynthesis Research.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(23):2013-2032. doi: 10.2174/0115680266305274240723120426. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39136504 Review.
-
Advances in the biosynthesis of naturally occurring benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 30;16:1548471. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1548471. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39949415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF gene family in Coptis Chinensis Franch reveals its role in tissue-specific accumulation of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 16;25(1):972. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10883-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39415101 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

