Dual-energy CT for gastrointestinal bleeding
- PMID: 37035764
- PMCID: PMC10077409
- DOI: 10.1259/bjro.20220054
Dual-energy CT for gastrointestinal bleeding
Abstract
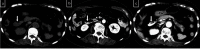
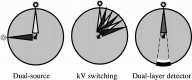
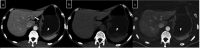
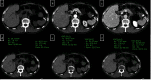
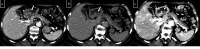
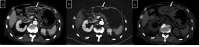
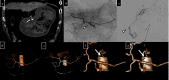
Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) can be used for various types of analyses, including iodine quantification, and its usefulness in diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases has been reported. This pictorial review describes the use of DECT in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding. Virtual non-contrast computed tomography (CT) is available in DECT and can be used as a substitute for pre-contrast CT in the case of gastrointestinal haemorrhage. The omission of pre-contrast CT can reduce radiation exposure by approximately 30%. A low-keV virtual monochromatic X-ray image (VMI) can increase the contrast of iodine, and iodine maps can provide better visibility of extravasation. These analytical images can provide a diagnosis with a high degree of confidence. In addition, the low-keV VMI clearly illustrates the vascular structure, which may be useful for improving the visibility of vascular lesions and for confirming the arterial anatomy before embolisation. Considering that these analytical images are created on the basis of contrast-enhanced CT, the positional information of organs is entirely identical, thus allowing the comparison of images regardless of intestinal peristalsis or body motion. In conclusion, the analytical images of DECT can solve the problems of conventional protocols, and DECT is considered useful in the imaging diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual-layer DECT for multiphasic hepatic CT with 50 percent iodine load: a matched-pair comparison with a 120 kVp protocol.Eur Radiol. 2018 Apr;28(4):1719-1730. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5114-3. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29063254
-
Rapid switching kVp dual energy CT: Value of reconstructed dual energy CT images and organ dose assessment in multiphasic liver CT exams.Eur J Radiol. 2018 May;102:102-108. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.02.022. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29685522 Free PMC article.
-
Noise reduction approach in pediatric abdominal CT combining deep learning and dual-energy technique.Eur Radiol. 2021 Apr;31(4):2218-2226. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07349-9. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33030573
-
Dual energy imaging in cardiothoracic pathologies: A primer for radiologists and clinicians.Eur J Radiol Open. 2021 Jan 20;8:100324. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2021.100324. eCollection 2021. Eur J Radiol Open. 2021. PMID: 33532519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Implementation of Dual-Energy CT for Gastrointestinal Imaging.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Sep;217(3):651-663. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.25093. Epub 2020 Dec 30. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. PMID: 33377415 Review.
Cited by
-
Thoracic Diseases: Technique and Applications of Dual-Energy CT.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;13(14):2440. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142440. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510184 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

