Pathogenicity of a novel bovine adenovirus type 3 with a natural deletion partial fiber gene in BALB/c mice
- PMID: 37035797
- PMCID: PMC10076824
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1138159
Pathogenicity of a novel bovine adenovirus type 3 with a natural deletion partial fiber gene in BALB/c mice
Abstract
Objective: A novel Bovine adenovirus type 3 (BAdV-3) with a natural deletion partial fiber gene was isolated in 2020 and named BO/YB24/17/CH. The objective of this study was to understand the pathogenicity of this virus.
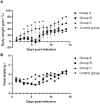
Methods: Thiry-two 3-week-old BALB/c mice were divided into three experimental groups and a control group. Mice in the experimental groups were intranasally inoculated with virus, and mice in the control group were inoculated with MDBK cell supernatant. Mice were weighed and clinically examined daily for appearance of any clinical signs. Three infected mice and one control mouse were euthanized at 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15 days after inoculation. Tissue samples were collected for histopathological examination, immunohistochemical staining, and detection of the replication dynamics of virus.
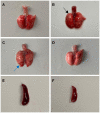
Results: All infected mice developed mild clinical signs such as lethargy, weight loss, loss of appetite, and a rough hair coat, and gross lesions were observed as pulmonary punctate hemorrhage, lobular atrophy and splenomegaly. Histopathological examination revealed thickening of alveolar septa and mildly dilated splenic nodules and blurred red-white medullary demarcation in the spleen. Immunohistochemical results further confirmed that the production of the above lesions was due to viral infection. Importantly, unlike previously reported BAdV-3 detection only in the lungs and trachea, this isolate could be detected in multiple organs such as the heart, liver, spleen, kidney, and even blood by virus isolation and titration and real-time PCR methods.
Clinical significance: This study provides further insight into the pathogenicity of the fiber region deletion strain BO/YB24/17/CH in BALB/c mice, which provides a reference for the prevention and control of BAdV-3 as well as the development of vaccines.
Keywords: BALB/c mice; bovine adenovirus type 3; deleted strain; fiber gene; pathogenicity.
Copyright © 2023 Li, He, Zou, Yue, Tang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

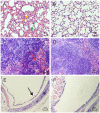
 ) marked congestion and hemorrhage, and (
) marked congestion and hemorrhage, and ( ) alveolar septal thickening (400×). (B) Normal control lung sections from mock-inoculated mice did not show observable histological changes (400×). (C) 5 days after infection, the spleens of mice showed (
) alveolar septal thickening (400×). (B) Normal control lung sections from mock-inoculated mice did not show observable histological changes (400×). (C) 5 days after infection, the spleens of mice showed ( ) blurred red-white medullary demarcation (400×). (D) Normal control spleen sections from mock-inoculated mice did not show observable histological changes (400×). (E) 13 days after infection, the tracheas of mice showed (
) blurred red-white medullary demarcation (400×). (D) Normal control spleen sections from mock-inoculated mice did not show observable histological changes (400×). (E) 13 days after infection, the tracheas of mice showed ( ) detached epithelial cells (400×). (F) Normal control trachea sections from mock-inoculated mice showing no observable histological changes (400×).
) detached epithelial cells (400×). (F) Normal control trachea sections from mock-inoculated mice showing no observable histological changes (400×).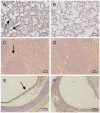
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and characteristics of a novel bovine adenovirus type 3 with a natural deletion fiber gene.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Sep;83:104348. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104348. Epub 2020 May 4. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32380313
-
Pathogenesis of a genotype C strain of bovine parainfluenza virus type 3 infection in albino guinea pigs.Virus Res. 2014 Aug 8;188:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24681303
-
Clinicopathological features of 11 suspected outbreaks of bovine adenovirus infection and development of a real-time quantitative PCR to detect bovine adenovirus type 10.N Z Vet J. 2016 Sep;64(5):308-13. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2016.1198280. Epub 2016 Jun 26. N Z Vet J. 2016. PMID: 27277320
-
Molecular characterization of a bovine adenovirus type 7 (Bovine Atadenovirus F) strain isolated from a systemically infected calf in Germany.Virol J. 2022 May 24;19(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01817-y. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35610654 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of a Chinese strain of bovine adenovirus type 3 infection in albino guinea pigs.Arch Virol. 2014 Dec;159(12):3211-8. doi: 10.1007/s00705-014-2181-5. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Arch Virol. 2014. PMID: 25119675
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

