Angiotensin II-Mediated Neuroinflammation in the Hippocampus Contributes to Neuronal Deficits and Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure Rats
- PMID: 37035922
- PMCID: PMC10192104
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21070
Angiotensin II-Mediated Neuroinflammation in the Hippocampus Contributes to Neuronal Deficits and Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure Rats
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is a debilitating disease affecting >64 million people worldwide. In addition to impaired cardiovascular performance and associated systemic complications, most patients with HF suffer from depression and substantial cognitive decline. Although neuroinflammation and brain hypoperfusion occur in humans and rodents with HF, the underlying neuronal substrates, mechanisms, and their relative contribution to cognitive deficits in HF remains unknown.
Methods: To address this critical gap in our knowledge, we used a well-established HF rat model that mimics clinical outcomes observed in the human population, along with a multidisciplinary approach combining behavioral, electrophysiological, neuroanatomical, molecular and systemic physiological approaches.
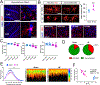
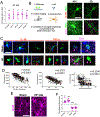
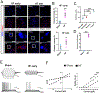
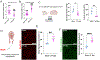
Results: Our studies support neuroinflammation, hypoperfusion/hypoxia, and neuronal deficits in the hippocampus of HF rats, which correlated with the progression and severity of the disease. An increased expression of AT1aRs (Ang II [angiotensin II] receptor type 1a) in hippocampal microglia preceded the onset of neuroinflammation. Importantly, blockade of AT1Rs with a clinically used therapeutic drug (Losartan), and delivered in a clinically relevant manner, efficiently reversed neuroinflammatory end points (but not hypoxia ones), resulting in turn in improved cognitive performance in HF rats. Finally, we show than circulating Ang II can leak and access the hippocampal parenchyma in HF rats, constituting a possible source of Ang II initiating the neuroinflammatory signaling cascade in HF.
Conclusions: In this study, we identified a neuronal substrate (hippocampus), a mechanism (Ang II-driven neuroinflammation) and a potential neuroprotective therapeutic target (AT1aRs) for the treatment of cognitive deficits in HF.
Keywords: angiotensin II; depression; heart failure; hippocampus; microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-II drives changes in microglia-vascular interactions in rats with heart failure.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):1537. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07229-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39562706 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II Causes Apoptosis of Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells and Memory Impairment Through the Action on AMPK-PGC1α Signaling in Heart Failure.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Jun;6(6):1491-1503. doi: 10.1002/sctm.16-0382. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28244243 Free PMC article.
-
Neurocognitive Disorders in Heart Failure: Novel Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underpinning Memory Loss and Learning Impairment.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;56(12):8035-8051. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01655-0. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31165973 Review.
-
Cognitive impairment in heart failure is associated with altered Wnt signaling in the hippocampus.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Aug 25;11(16):5924-5942. doi: 10.18632/aging.102150. Epub 2019 Aug 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31447429 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Heat Stress on Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Insights into the Cellular and Molecular Basis of Neuroinflammation-Induced Deficits.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;43(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01165-5. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 34767143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the role of brain renin angiotensin system in vascular dementia: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives.Exp Brain Res. 2025 Apr 26;243(5):130. doi: 10.1007/s00221-025-07072-1. Exp Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40285869 Review.
-
Neuroimmunology of Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2024 Jul;26(7):339-347. doi: 10.1007/s11906-024-01301-8. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2024. PMID: 38613621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-II drives changes in microglia-vascular interactions in rats with heart failure.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):1537. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07229-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39562706 Free PMC article.
-
Increased absorptive transcytosis and tight junction weakness in heart failure are equally corrected by exercise training and losartan.Clin Sci (Lond). 2025 May 20;139(11):527-43. doi: 10.1042/CS20242965. Online ahead of print. Clin Sci (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40395026 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Impairment and Synaptic Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Disorders: The New Frontiers of the Heart-Brain Axis.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 18;12(10):2387. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102387. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hammond CA, Blades NJ, Chaudhry SI, Dodson JA, Longstreth WT Jr., Heckbert SR, Psaty BM, Arnold AM, Dublin S, Sitlani CM, et al. Long-Term Cognitive Decline After Newly Diagnosed Heart Failure: Longitudinal Analysis in the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study). Circ Heart Fail. 2018;11:e004476. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004476 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

