MHC Class I Ligands of Rhesus Macaque Killer Cell Ig-like Receptors
- PMID: 37036309
- PMCID: PMC10192222
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200954
MHC Class I Ligands of Rhesus Macaque Killer Cell Ig-like Receptors
Abstract
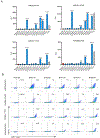
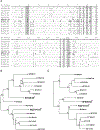
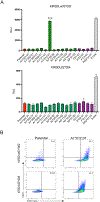
Definition of MHC class I ligands of rhesus macaque killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIRs) is fundamental to NK cell biology in this species as an animal model for infectious diseases, reproductive biology, and transplantation. To provide a more complete foundation for studying NK cell responses, rhesus macaque KIRs representing common allotypes of lineage II KIR genes were tested for interactions with MHC class I molecules representing diverse Macaca mulatta (Mamu)-A, -B, -E, -F, -I, and -AG alleles. KIR-MHC class I interactions were identified by coincubating reporter cell lines bearing chimeric KIR-CD3ζ receptors with target cells expressing individual MHC class I molecules and were corroborated by staining with KIR IgG-Fc fusion proteins. Ligands for 12 KIRs of previously unknown specificity were identified that fell into three general categories: interactions with multiple Mamu-Bw4 molecules, interactions with Mamu-A-related molecules, including allotypes of Mamu-AG and the hybrid Mamu-B*045:03 molecule, or interactions with Mamu-A1*012:01. Whereas most KIRs found to interact with Mamu-Bw4 are inhibitory, most of the KIRs that interact with Mamu-AG are activating. The KIRs that recognize Mamu-A1*012:01 belong to a phylogenetically distinct group of macaque KIRs with a 3-aa deletion in the D0 domain that is also present in human KIR3DL1/S1 and KIR3DL2. This study more than doubles the number of rhesus macaque KIRs with defined MHC class I ligands and identifies interactions with Mamu-AG, -B*045, and -A1*012. These findings support overlapping, but nonredundant, patterns of ligand recognition that reflect extensive functional diversification of these receptors.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Parham P 2005. MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat. Rev. Immunol 5: 201–214. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL 2005. NK cell recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol 23: 225–274. - PubMed
-
- Huard B, and Fruh K. 2000. A role for MHC class I down-regulation in NK cell lysis of herpes virus-infected cells. Eur. J. Immunol 30: 509–515. - PubMed
-
- Falk CS, Mach M, Schendel DJ, Weiss EH, Hilgert I, and Hahn G. 2002. NK cell activity during human cytomegalovirus infection is dominated by US2–11-mediated HLA class I down-regulation. J. Immunol 169: 3257–3266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

