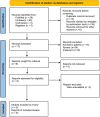
Relationship Between Breast Cancer Risk and Polymorphisms in CLOCK Gene: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37036639
- PMCID: PMC10665245
- DOI: 10.1007/s10528-023-10372-2
Relationship Between Breast Cancer Risk and Polymorphisms in CLOCK Gene: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
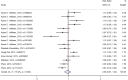
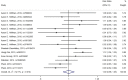
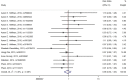
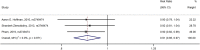
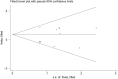
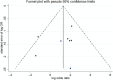
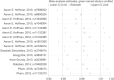
Previous studies found that the circadian clock gene participated in the genesis and development of breast cancer. However, research findings on the relationship between polymorphisms in the CLOCK gene and breast cancer risk were inconsistent. This study performed a meta-analysis of the association between CLOCK gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk. PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases were electronically searched to collect studies on the association between CLOCK gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk from inception to February 14, 2022. The quality of the included literature was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. For statistical analysis, odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using STATA 14.0. In addition, publication bias was performed by the funnel diagram and the Harbord's regression test. And sensitivity analysis was assessed by the trim and fill method. A total of 6 eligible studies, including 10,164 subjects (5488 breast cancer cases and 4676 controls), were screened in this meta-analysis. Though we did not find a significant association between the polymorphisms in the overall CLOCK gene with breast cancer risk [OR (95%CI) = 0.98 (0.96, 1.01), P = 0.148], we found that compared with T/T types of rs3749474 in CLOCK, T/C and C/C types of rs3749474 were associated with lower risk of breast cancer [OR (95%CI) = 0.93 (0.88, 0.98), P = 0.003]. The sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of the results. The funnel plot showed no significant publication bias. Polymorphisms in the CLOCK gene might be associated with breast cancer risk. More studies are needed to confirm the conclusion.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CLOCK gene; Meta-analysis; Polymorphisms.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Camblor Murube M, Borregon-Rivilla E, Colmenarejo G, Aguilar-Aguilar E, Martínez JA, Ramírez De Molina A, Reglero G, Loria-Kohen V. Polymorphism of CLOCK gene rs3749474 as a modulator of the circadian evening carbohydrate intake impact on nutritional status in an adult sample. Nutrients. 2020 doi: 10.3390/nu12041142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

