RPL26/uL24 UFMylation is essential for ribosome-associated quality control at the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 37036982
- PMCID: PMC10120006
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2220340120
RPL26/uL24 UFMylation is essential for ribosome-associated quality control at the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
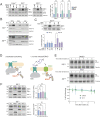
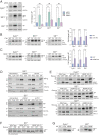
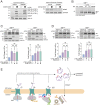
Ribosomes that stall while translating cytosolic proteins are incapacitated by incomplete nascent chains, termed "arrest peptides" (APs) that are destroyed by the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) via a process known as the ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathway. By contrast, APs on ribosomes that stall while translocating secretory proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER-APs) are shielded from cytosol by the ER membrane and the tightly sealed ribosome-translocon junction (RTJ). How this junction is breached to enable access of cytosolic UPS machinery and 26S proteasomes to translocon- and ribosome-obstructing ER-APs is not known. Here, we show that UPS and RQC-dependent degradation of ER-APs strictly requires conjugation of the ubiquitin-like (Ubl) protein UFM1 to 60S ribosomal subunits at the RTJ. Therefore, UFMylation of translocon-bound 60S subunits modulates the RTJ to promote access of proteasomes and RQC machinery to ER-APs.
Keywords: UFM1; UFMylation; endoplasmic reticulum; ribosome-associated quality control; ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Update of
-
RPL26/uL24 UFMylation is essential for ribosome-associated quality control at the endoplasmic reticulum.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 9:2023.03.08.531792. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.08.531792. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Apr 18;120(16):e2220340120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220340120. PMID: 36945571 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

