Impact of HER2 on prognosis and benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II/III gastric cancer patients: a multicenter observational study
- PMID: 37037586
- PMCID: PMC10389606
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000370
Impact of HER2 on prognosis and benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II/III gastric cancer patients: a multicenter observational study
Abstract
Background: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a well-developed therapeutic target in breast and gastric cancer (GC). However, the impact of HER2 on survival and benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy remains unclear in patients with GC.
Materials and methods: This multicenter cohort study involved 5622 consecutive stage II/III GC patients. HER2 expression was assessed prospectively via immunohistochemistry (IHC). The staining intensity was graded on a scale of 0 to 3+. An IHC score of 2+or 3+was defined as high expression, and a score of 3+was defined as overexpression.
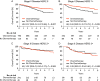
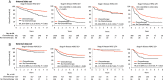
Results: HER2 overexpression was independently associated with a lower 5-year overall survival (OS) in stage II [hazard ratio (HR), 2.10; 95% CI: 1.41-3.11], but not in stage III GC (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.82-1.20). Further analysis revealed that stage II patients with high HER2 expression showed a poorer response to chemotherapy than stage II patients with low HER2 expression ( Pinteraction =0.024). The HRs for 5-year OS were 0.51 (95% CI, 0.38-0.70) for stage II patients with low HER2 expression, 0.58 (95% CI, 0.51-0.66) for stage III patients with low HER2 expression, 1.13 (95% CI, 0.61-2.09) for stage II patients with high HER2 expression, and 0.47 (95% CI, 0.36-0.61) for stage III patients with high HER2 expression.
Conclusions: Fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy is insufficient for stage II GC patients with high HER2 expression, indicating that prospective trials are required to validate alternative HER2-targeted adjuvant therapies in the individuals above.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Oh DY, Bang YJ. HER2-targeted therapies – a role beyond breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2020;17:33–48. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. . Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;376:687–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

