Comparison of two multi-trait association testing methods and sequence-based fine mapping of six additive QTL in Swiss Large White pigs
- PMID: 37038103
- PMCID: PMC10084639
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09295-4
Comparison of two multi-trait association testing methods and sequence-based fine mapping of six additive QTL in Swiss Large White pigs
Abstract
Background: Genetic correlations between complex traits suggest that pleiotropic variants contribute to trait variation. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) aim to uncover the genetic underpinnings of traits. Multivariate association testing and the meta-analysis of summary statistics from single-trait GWAS enable detecting variants associated with multiple phenotypes. In this study, we used array-derived genotypes and phenotypes for 24 reproduction, production, and conformation traits to explore differences between the two methods and used imputed sequence variant genotypes to fine-map six quantitative trait loci (QTL).
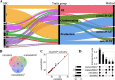
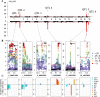
Results: We considered genotypes at 44,733 SNPs for 5,753 pigs from the Swiss Large White breed that had deregressed breeding values for 24 traits. Single-trait association analyses revealed eleven QTL that affected 15 traits. Multi-trait association testing and the meta-analysis of the single-trait GWAS revealed between 3 and 6 QTL, respectively, in three groups of traits. The multi-trait methods revealed three loci that were not detected in the single-trait GWAS. Four QTL that were identified in the single-trait GWAS, remained undetected in the multi-trait analyses. To pinpoint candidate causal variants for the QTL, we imputed the array-derived genotypes to the sequence level using a sequenced reference panel consisting of 421 pigs. This approach provided genotypes at 16 million imputed sequence variants with a mean accuracy of imputation of 0.94. The fine-mapping of six QTL with imputed sequence variant genotypes revealed four previously proposed causal mutations among the top variants.
Conclusions: Our findings in a medium-size cohort of pigs suggest that multivariate association testing and the meta-analysis of summary statistics from single-trait GWAS provide very similar results. Although multi-trait association methods provide a useful overview of pleiotropic loci segregating in mapping populations, the investigation of single-trait association studies is still advised, as multi-trait methods may miss QTL that are uncovered in single-trait GWAS.
Keywords: Genome-wide association study; Imputation; Meta-analyses; Multivariate analyses; Pleiotropy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AH is employee of SUISAG (the Swiss pig breeding and competence centre). HP is a member of the editorial board of BMC Genomics. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

