Involvement of Transforming Growth Factor-β-Associated Kinase 1 in Fixed Airway Obstruction in Asthmatic Patients with Longer Disease Duration Independent on Airway Eosinophilia
- PMID: 37038432
- PMCID: PMC10082578
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S403645
Involvement of Transforming Growth Factor-β-Associated Kinase 1 in Fixed Airway Obstruction in Asthmatic Patients with Longer Disease Duration Independent on Airway Eosinophilia
Abstract
Objective: Transforming growth factor-β-associated kinase 1 (TAK1) mediates non-canonical TGF-β signalling by promoting adhesive, migratory, proliferative and contractile responses of fibroblasts to TGF-β1. However, TAK1 expression status in asthmatic patients with or without fixed airway obstruction (FAO) is unknown.
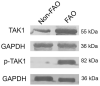
Patients and methods: A total of 60 adult asthmatics with FAO were recruited and compared to 43 those without FAO (nFAO). TGF-β1 concentrations, and total TAK1 and phosphorylated TAK1 (p-TAK1) levels were determined in sputum supernatants, cytospin, and whole cell lysate by ELISA, immunocytochemistry, and Western blot analysis, respectively, in asthmatics with and without FAO.
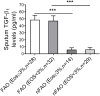
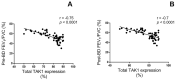
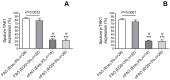
Results: Asthmatic patients with FAO had much greater sputum TGF-β1 concentrations than those without FAO. This was independent of airway eosinophilia as there was no significant difference in TGF-β1 levels between high and low eosinophil counts within FAO and nFAO groups. In contrast, patients with FAO in the presence of sputum eosinophilia had greater expression of TAK1 and p-TAK1 than those without sputum eosinophilia (P=0.0032 and P=0.0061, respectively). The Western Blot data of total TAK1 and p-TAK1 were consistent with the immunocytochemistry, showing upregulation in all sputum cell types (neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages, lymphocytes and airway epithelial cells). In addition, total TAK1 expression negatively correlated with pre- and post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio.
Conclusion: TAK1 may play a key role in asthmatic patients with fixed airway obstruction, which was independent of eosinophilic airway inflammation. The interruption of TAK1 might have favourable clinical impact.
Keywords: asthma; fixed airway obstruction; transforming growth factor-β-associated kinase 1.
© 2023 Maneechotesuwan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and biological factors associated with irreversible airway obstruction in adult asthma.Respir Med. 2020 Dec;175:106202. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106202. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33202369
-
Distinct profile of inflammatory and remodelling biomarkers in sputum of severe asthmatic patients with or without persistent airway obstruction.World Allergy Organ J. 2019 Dec 9;12(11):100078. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2019.100078. eCollection 2019 Nov. World Allergy Organ J. 2019. PMID: 31871533 Free PMC article.
-
Increased production of TGF-β1 from sputum cells of COPD: Relationship with airway obstruction.Cytokine. 2017 Nov;99:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.06.018. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 28668545
-
Inflammatory patterns in fixed airflow obstruction are dependent on the presence of asthma.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 3;15(12):e0243109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243109. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33270766 Free PMC article.
-
Asthma and fixed airflow obstruction: Long-term trajectories suggest distinct endotypes.Clin Exp Allergy. 2021 Jan;51(1):39-48. doi: 10.1111/cea.13714. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2021. PMID: 32706916
Cited by
-
CAR-NKT Cells in Asthma: Use of NKT as a Promising Cell for CAR Therapy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Jun;66(3):328-362. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08998-0. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38995478 Review.
-
N-cadherin antagonism is bronchoprotective in severe asthma models.Sci Adv. 2024 Nov 29;10(48):eadp8872. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp8872. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39612338 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

