Polydopamine Nanoparticles-Based Photothermal Effect Against Adhesion Formation in a Rat Model of Achilles Tendon Laceration Repair
- PMID: 37038441
- PMCID: PMC10082603
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S393454
Polydopamine Nanoparticles-Based Photothermal Effect Against Adhesion Formation in a Rat Model of Achilles Tendon Laceration Repair
Abstract
Background: Adhesion formation after tendon surgery is a major obstacle to repair of tendon ruptures, and there is still no effective clinical anti-adhesion method. Myofibroblasts expressing α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) play a crucial role in adhered fibrous tissue. Heat shock protein (Hsp) 72 can selectively prevent the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which mediates the conversion from fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. The purpose of this study was to investigate for the first time whether polydopamine nanoparticles (PDA NPs)-based photothermal effect would attenuate adhesion formation in a rat model of Achilles tendon laceration repair.
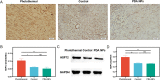
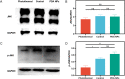
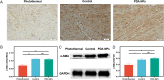
Materials and methods: Forty-five adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to the photothermal group, the control group and the PDA NPs group (n = 15 per group). The primary outcome measure was the adhesion scores at two weeks after surgery according to the grading of Tang et al. The secondary outcomes included the expressions of Hsp 72, JNK, phosphorylated JNK and α-SMA, which were measured by immunohistochemistry or Western blot.
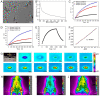
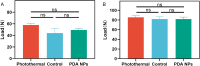
Results: The average adhesion score was significantly lower in the photothermal group (4.25 ± 0.21) than that in the control group (5.29 ± 0.12) (p = 0.005) and the PDA NPs group (5.29 ± 0.20) (p = 0.005). Relative to the control group and PDA NPs group, Hsp 72 in the photothermal group was significantly increased whereas α-SMA and p-JNK was significantly decreased, but JNK was not found to be different across the three groups.
Conclusion: The photothermal effect produced by PDA NPs could reduce tendon adhesion formation in rats by inhibiting myocyte fibrosis, which may have potential in developing endogenous heating for postsurgical tissue adhesions.
Keywords: adhesion formation; photothermal effects; polydopamine nanoparticle; tendon.
© 2023 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Combined Verapamil-Polydopamine Nanoformulation Inhibits Adhesion Formation in Achilles Tendon Injury Using Rat Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jan 6;18:115-126. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S377600. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36636643 Free PMC article.
-
Photothermal Treatment of Polydopamine Nanoparticles@Hyaluronic Acid Methacryloyl Hydrogel Against Peripheral Nerve Adhesion in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 May 23;18:2777-2793. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S410092. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37250473 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on anti-adhesion effect and mechanism of dynamic and static stress stimulation during early healing process of rat Achilles tendon injury].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 15;38(11):1391-1398. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202405090. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39542633 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Outcomes and Complications of Open Versus Minimally Invasive Repair of Acute Achilles Tendon Ruptures: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Mar;51(3):825-836. doi: 10.1177/03635465211053619. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 34908499
-
Polydopamine, harness of the antibacterial potentials-A review.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Jun 16;15:100329. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100329. eCollection 2022 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35757029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Carbon Dots and Ursolic Acid Co-Encapsulated Liposomes Composite Hydrogel for Alleviating Adhesion Formation and Enhancing Tendon Healing in Tendon Injury.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 27;19:8709-8727. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S466312. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39220191 Free PMC article.
-
The Induction of Combined Hyperthermal Ablation Effect of Irreversible Electroporation with Polydopamine Nanoparticle-Coated Electrodes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 13;25(8):4317. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084317. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673901 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

