Cardiac Sarcoidosis With Elevated Cardiac Troponin Mimicking Acute Myocardial Ischemia: A Case Report
- PMID: 37038571
- PMCID: PMC10082640
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.35948
Cardiac Sarcoidosis With Elevated Cardiac Troponin Mimicking Acute Myocardial Ischemia: A Case Report
Abstract
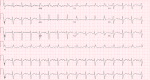
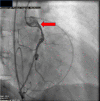
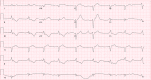
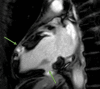
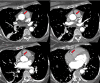
Cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) is a disease entity with variable presentation causing significant morbidity and mortality. Concurrent signs of myocardial injury as evidenced by troponin elevation add to the complexity of an already challenging diagnosis. We present an unusual case of CS with elevated troponin I mimicking an acute ischemic cardiac event. A 48-year-old female presented with a two-month history of presyncope. Electrocardiogram showed a bifascicular block with concomitant significant troponin I elevation. Two-dimensional echocardiography showed new-onset left ventricular systolic dysfunction with an ejection fraction of 40-45%. A heparin drip was initiated for possible non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Coronary angiography showed no evidence of epicardial coronary artery disease but did show an anomalous right coronary artery; however, CT angiography did not reveal any significant stenosis. Further, the telemetry monitor captured intermittent complete atrioventricular blocks. Due to concerns for an infiltrative cardiac disease, a cardiac magnetic resonance was done showing findings consistent with possible CS. CT scan of the chest showed no radiographic evidence of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scan showed findings of active inflammation in the myocardium consistent with possible CS. The patient was treated for clinical CS with systemic corticosteroids and methotrexate. Follow-up six weeks later showed clinical improvement of symptoms. Our clinical case encompasses the unique variable presentation of CS including cardiac conduction abnormalities and left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Concomitant troponin I elevation can mimic myocardial ischemia, making the diagnosis more challenging. Treatment strategies aim to mitigate the long-term effects of CS on the heart; however, there is a paucity of data for appropriate pharmacological regimens.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; cardiac sarcoidosis; case report; sarcoidosis; troponin elevation.
Copyright © 2023, Casipit et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac sarcoidosis presenting with syncope and rapidly progressive atrioventricular block: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2018 Oct 11;2(4):yty103. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/yty103. eCollection 2018 Dec. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 31020179 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of myocardial viability: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(15):1-45. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074392 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected Case of Cardiac Sarcoidosis in a Caucasian Male.Cureus. 2023 Jan 4;15(1):e33353. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33353. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36751252 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac sarcoidosis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Aug;31(4):428-41. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1262211. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20665393 Review.
-
Contemporary NSTEMI management: the role of the hospitalist.Hosp Pract (1995). 2020 Feb;48(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/21548331.2020.1701329. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Hosp Pract (1995). 2020. PMID: 31815570 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
