Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Amyloid-β Plaques in a Murine Alzheimer's Disease Model
- PMID: 37038807
- PMCID: PMC10200222
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-220198
Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Amyloid-β Plaques in a Murine Alzheimer's Disease Model
Abstract
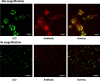
Background: Early detection of amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregates is a critical step to improve the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) because neuronal damage by the Aβ aggregates occurs before clinical symptoms are apparent. We have previously shown that luminescent conjugated oligothiophenes (LCOs), which are highly specific towards protein aggregates of Aβ, can be used to fluorescently label amyloid plaque in living rodents.
Objective: We hypothesize that the LCO can be used to target gadolinium to the amyloid plaque and hence make the plaque detectable by T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
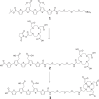
Methods: A novel LCO-gadolinium construct was synthesized to selectively bind to Aβ plaques and give contrast in conventional T1-weighted MR images after intravenous injection in Tg-APPSwe mice.
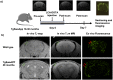
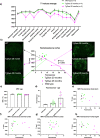
Results: We found that mice with high plaque-burden could be identified using the LCO-Gd constructs by conventional MRI.
Conclusion: Our study shows that MR imaging of amyloid plaques is challenging but feasible, and hence contrast-mediated MR imaging could be a valuable tool for early AD detection.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-β (Aβ); fluorescence; magnetic resonance imaging; multimodal imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gd-nanoparticles functionalization with specific peptides for ß-amyloid plaques targeting.J Nanobiotechnology. 2016 Jul 25;14(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12951-016-0212-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016. PMID: 27455834 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targeting of Alzheimer's amyloid plaques for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.Neurobiol Dis. 2002 Nov;11(2):315-29. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0550. Neurobiol Dis. 2002. PMID: 12505424
-
In vivo targeting and multimodal imaging of cerebral amyloid-β aggregates using hybrid GdF3 nanoparticles.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022 Dec;17(29):2173-2187. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2022-0252. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36927004
-
Amyloid imaging using high-field magnetic resonance.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2010;9(3):95-9. doi: 10.2463/mrms.9.95. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20885081 Review.
-
APP transgenic modeling of Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms of neurodegeneration and aberrant neurogenesis.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):111-26. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0232-6. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 20091183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rose SE, Janke AL, Chalk JB (2008) Gray and white matter changes in Alzheimer’s disease: A diffusion tensor imaging study, J Magn Reson Imaging 27, 20–26. - PubMed
-
- Bateman RJ, Xiong C, Benzinger TL, Fagan AM, Goate A, Fox NC, Marcus DS, Cairns NJ, Xie X, Blazey TM, Holtzman DM, Santacruz A, Buckles V, Oliver A, Moulder K, Aisen PS, Ghetti B, Klunk WE, McDade E, Martins RN, Masters CL, Mayeux R, Ringman JM, Rossor MN, Schofield PR, Sperling RA, Salloway S, Morris JC, Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (2012) Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease, N Engl J Med 367, 795–804. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chételat G, Arbizu J, Barthel H, Garibotto V, Law I, Morbelli S, van de Giessen E, Agosta F, Barkhof F, Brooks DJ, Carrillo MC, Dubois B, Fjell AM, Frisoni GB, Hansson O, Herholz K, Hutton BF, Jack CR Jr, Lammertsma AA, Landau SM, Minoshima S, Nobili F, Nordberg A, Ossenkoppele R, Oyen WJG, Perani D, Rabinovici GD, Scheltens P, Villemagne VL, Zetterberg H, Drzezga A (2020) Amyloid-PET and (18)F-FDG-PET in the diagnostic investigation of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, Lancet Neurol 19, 951–962. - PubMed
-
- Åslund A, Sigurdson CJ, Klingstedt T, Grathwohl S, Bolmont T, Dickstein DL, Glimsdal E, Prokop S, Lindgren M, Konradsson P, Holtzman DM, Hof PR, Heppner FL, Gandy S, Jucker M, Aguzzi A, Hammarström P, Nilsson KPR (2009) Novel pentameric thiophenederivatives for in vitro and in vivo optical imaging of aplethora of protein aggregates in cerebral amyloidoses, ACSChem Biol 4, 673–684. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

