Challenges in the combination of radiotherapy and immunotherapy for breast cancer
- PMID: 37039098
- PMCID: PMC10929662
- DOI: 10.1080/14737140.2023.2188196
Challenges in the combination of radiotherapy and immunotherapy for breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Immunotherapy (IT) is showing promise in the treatment of breast cancer, but IT alone only benefits a minority of patients. Radiotherapy (RT) is usually included in the standard of care for breast cancer patients and is traditionally considered as a local form of treatment. The emerging knowledge of RT-induced systemic immune response, and the observation that the rare abscopal effect of RT on distant cancer metastases can be augmented by IT, have increased the enthusiasm for combinatorial immunoradiotherapy (IRT) for breast cancer patients. However, IRT largely follows the traditional sole RT and IT protocols and does not consider patient specificity, although patients' responses to treatment remain heterogeneous.
Areas covered: This review discusses the rationale of IRT for breast cancer, the current knowledge, challenges, and future directions.
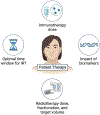
Expert opinion: The synergy between RT and the immune system has been observed but not well understood at the basic level. The optimal dosages, timing, target, and impact of biomarkers are largely unknown. There is an urgent need to design efficacious pre-clinical and clinical trials to optimize IRT for cancer patients, maximize the synergy of radiation and immune response, and explore the abscopal effect in depth, taking into account patients' personal features.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; abscopal effect; breast cancer; immune response; precision medicine; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
