Evidence-based consensus guidelines for the management of catatonia: Recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology
- PMID: 37039129
- PMCID: PMC10101189
- DOI: 10.1177/02698811231158232
Evidence-based consensus guidelines for the management of catatonia: Recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology
Abstract
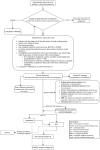
The British Association for Psychopharmacology developed an evidence-based consensus guideline on the management of catatonia. A group of international experts from a wide range of disciplines was assembled. Evidence was gathered from existing systematic reviews and the primary literature. Recommendations were made on the basis of this evidence and were graded in terms of their strength. The guideline initially covers the diagnosis, aetiology, clinical features and descriptive epidemiology of catatonia. Clinical assessments, including history, physical examination and investigations are then considered. Treatment with benzodiazepines, electroconvulsive therapy and other pharmacological and neuromodulatory therapies is covered. Special regard is given to periodic catatonia, malignant catatonia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome and antipsychotic-induced catatonia. There is attention to the needs of particular groups, namely children and adolescents, older adults, women in the perinatal period, people with autism spectrum disorder and those with certain medical conditions. Clinical trials were uncommon, and the recommendations in this guideline are mainly informed by small observational studies, case series and case reports, which highlights the need for randomised controlled trials and prospective cohort studies in this area.
Keywords: Catatonia; benzodiazepine; catatonic schizophrenia; electroconvulsive therapy; guideline; neuroleptic malignant syndrome; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article: NA, SA, ASD, AF, S Grover, DH, DK, GL, SCM, GN, LEW, TS, JEW, S Gee and AW declare no conflicts of interest.
MAO is one of the creators of the free videographic educational resources for the Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale mentioned in the guideline.
DSB is President of the BAP and KF is the Past President of the BAP.
GF is a consultant for Revival Therapeutics.
JPR is supported by the Wellcome Trust.
GL is supported by the Wellcome Trust and NIHR.
MSZ declares salary support to support research time from the NIHR UCLH BRC. MSZ declares honoraria for one lecture each for each of the four mentioned in the last 3 years: Norwegian Neurological Society; Copenhagen Neuropsychological Society, Rigshospitalet; Cygnet Healthcare; and UCB Pharma. MSZ declares travel and hotel support for a stay in Florence from the European Association of Neurology (EAN) for an EAN meeting on autoimmune encephalitis in April 2022. MSZ represents neurology in the UK for the Association of British Neurologists for matters related to Covid in meetings with NHS England and Royal College of Physicians.
AY is the Editor of Journal of Psychopharmacology and Deputy Editor, BJPsych Open. He has given paid lectures and has been on advisory boards for the following companies with drugs used in affective and related disorders: Astrazenaca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, LivaNova, Lundbeck, Sunovion, Servier, Livanova, Janssen, Allegan, Bionomics, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, COMPASS, Sage, Novartis and Neurocentrx. He is the principal investigator on the Restore-Life VNS registry study (funded by LivaNova); ESKETINTRD3004: ‘An Open-label, Long-term, Safety and Efficacy Study of Intranasal Esketamine in Treatment-resistant Depression’, ‘The Effects of Psilocybin on Cognitive Function in Healthy Participants’ and ‘The Safety and Efficacy of Psilocybin in Participants with Treatment-Resistant Depression (P-TRD)’. He is the UK Chief Investigator for Compass: COMP006 & COMP007 studies and for Novartis MDD study MIJ821A12201. He has received grant funding (past and present) from NIMH (USA); CIHR (Canada); NARSAD (USA); Stanley Medical Research Institute (USA); MRC (UK); Wellcome Trust (UK); Royal College of Physicians (Edin); BMA (UK); UBC-VGH Foundation (Canada); WEDC (Canada); CCS Depression Research Fund (Canada); MSFHR (Canada); NIHR (UK); Janssen (UK), and EU Horizon 2020. He has no shareholdings in pharmaceutical companies.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed A, Paramjit C, Bahar A. (2009) The treatment-resistant catatonia patient. Curr Psychiatry 8: 66.