The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effect of a classical hypnotic bromovalerylurea mediated by the activation of NRF2
- PMID: 37039781
- PMCID: PMC10372716
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvad030
The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effect of a classical hypnotic bromovalerylurea mediated by the activation of NRF2
Abstract
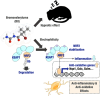
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (KEAP1-NRF2) system plays a central role in redox homeostasis and inflammation control. Oxidative stress or electrophilic compounds promote NRF2 stabilization and transcriptional activity by negatively regulating its inhibitor, KEAP1. We have previously reported that bromovalerylurea (BU), originally developed as a hypnotic, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in various inflammatory disease models. However, the molecular mechanism underlying its effect remains uncertain. Herein, we found that by real-time multicolor luciferase assay using stable luciferase red3 (SLR3) and green-emitting emerald luciferase (ELuc), BU potentiates NRF2-dependent transcription in the human hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2 cells, which lasted for more than 60 h. Further analysis revealed that BU promotes NRF2 accumulation and the transcription of its downstream cytoprotective genes in the HepG2 and the murine microglial cell line BV2. Keap1 knockdown did not further enhance NRF2 activity, suggesting that BU upregulates NRF2 by targeting KEAP1. Knockdown of Nfe2l2 in BV2 cells diminished the suppressive effects of BU on the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, like nitric oxide (NO) and its synthase NOS2, indicating the involvement of NRF2 in the anti-inflammatory effects of BU. These data collectively suggest that BU could be repurposed as a novel NRF2 activator to control inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: Abbreviations: ARE, antioxidant responsive element; BU, bromovalerylurea; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine 2; DMF, dimethyl fumarate; GCLC, glutamate–cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GCLM, glutamate–cysteine ligase modifier subunit; GSS, glutathione synthetase; GSH, glutathione; Hmox-1, heme oxygenase-1; IL-1β, interluekin-1β; IL-6, interluekin-6; JAK, Janus kinase; KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein; NO, nitric oxide; NOS2, NO synthase 2; NRE, NF-κB responsive element; NQO-1, NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2; TXNRD, thioredoxin–disulfide reductase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; KEAP1–NRF2; anti-inflammation; anti-oxidant oxygen; bromovalerylurea; drug action toxins/drugs/xenobiotics.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 May;94:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 26878775
-
[Mechanism of Tibetan medicine Ershiwuwei Songshi Pills against liver injury induced by acetaminophen in mice based on Keap1/Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-κB p65 signaling pathways].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Apr;47(8):2049-2055. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211103.707. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35531720 Chinese.
-
S-allylmercaptocysteine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via nuclear factor kappa B and Keap1/Nrf2 pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106273. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106273. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32070920
-
Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:645-657. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.022. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23892355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):108-146. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26122708 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sedanolide Activates KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway and Ameliorates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 20;24(22):16532. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216532. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003720 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

