Renin-Angiotensin System Modulation With Synthetic Angiotensin (1-7) and Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor-Biased Ligand in Adults With COVID-19: Two Randomized Clinical Trials
- PMID: 37039791
- PMCID: PMC10091180
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.3546
Renin-Angiotensin System Modulation With Synthetic Angiotensin (1-7) and Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor-Biased Ligand in Adults With COVID-19: Two Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
Importance: Preclinical models suggest dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection may increase the relative activity of angiotensin II compared with angiotensin (1-7) and may be an important contributor to COVID-19 pathophysiology.
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of RAS modulation using 2 investigational RAS agents, TXA-127 (synthetic angiotensin [1-7]) and TRV-027 (an angiotensin II type 1 receptor-biased ligand), that are hypothesized to potentiate the action of angiotensin (1-7) and mitigate the action of the angiotensin II.
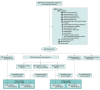
Design, setting, and participants: Two randomized clinical trials including adults hospitalized with acute COVID-19 and new-onset hypoxemia were conducted at 35 sites in the US between July 22, 2021, and April 20, 2022; last follow-up visit: July 26, 2022.
Interventions: A 0.5-mg/kg intravenous infusion of TXA-127 once daily for 5 days or placebo. A 12-mg/h continuous intravenous infusion of TRV-027 for 5 days or placebo.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was oxygen-free days, an ordinal outcome that classifies a patient's status at day 28 based on mortality and duration of supplemental oxygen use; an adjusted odds ratio (OR) greater than 1.0 indicated superiority of the RAS agent vs placebo. A key secondary outcome was 28-day all-cause mortality. Safety outcomes included allergic reaction, new kidney replacement therapy, and hypotension.
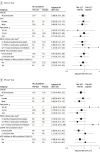
Results: Both trials met prespecified early stopping criteria for a low probability of efficacy. Of 343 patients in the TXA-127 trial (226 [65.9%] aged 31-64 years, 200 [58.3%] men, 225 [65.6%] White, and 274 [79.9%] not Hispanic), 170 received TXA-127 and 173 received placebo. Of 290 patients in the TRV-027 trial (199 [68.6%] aged 31-64 years, 168 [57.9%] men, 195 [67.2%] White, and 225 [77.6%] not Hispanic), 145 received TRV-027 and 145 received placebo. Compared with placebo, both TXA-127 (unadjusted mean difference, -2.3 [95% CrI, -4.8 to 0.2]; adjusted OR, 0.88 [95% CrI, 0.59 to 1.30]) and TRV-027 (unadjusted mean difference, -2.4 [95% CrI, -5.1 to 0.3]; adjusted OR, 0.74 [95% CrI, 0.48 to 1.13]) resulted in no difference in oxygen-free days. In the TXA-127 trial, 28-day all-cause mortality occurred in 22 of 163 patients (13.5%) in the TXA-127 group vs 22 of 166 patients (13.3%) in the placebo group (adjusted OR, 0.83 [95% CrI, 0.41 to 1.66]). In the TRV-027 trial, 28-day all-cause mortality occurred in 29 of 141 patients (20.6%) in the TRV-027 group vs 18 of 140 patients (12.9%) in the placebo group (adjusted OR, 1.52 [95% CrI, 0.75 to 3.08]). The frequency of the safety outcomes was similar with either TXA-127 or TRV-027 vs placebo.
Conclusions and relevance: In adults with severe COVID-19, RAS modulation (TXA-127 or TRV-027) did not improve oxygen-free days vs placebo. These results do not support the hypotheses that pharmacological interventions that selectively block the angiotensin II type 1 receptor or increase angiotensin (1-7) improve outcomes for patients with severe COVID-19.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04924660.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Lack of Benefit of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19.JAMA. 2023 Apr 11;329(14):1155-1156. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.4405. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37039803 No abstract available.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System Modulation in Adults With COVID-19.JAMA. 2023 Aug 15;330(7):663-664. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.10783. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37581678 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lauring AS, Tenforde MW, Chappell JD, et al. ; Influenza and Other Viruses in the Acutely Ill (IVY) Network . Clinical severity of, and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against, covid-19 from omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: prospective observational study. BMJ. 2022;376:e069761. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-069761 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams K, Rhoads JP, Surie D, et al. ; Influenza and Other Viruses in the Acutely Ill (IVY) Network . Vaccine effectiveness of primary series and booster doses against covid-19 associated hospital admissions in the United States: living test negative design study. BMJ. 2022;379:e072065. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-072065 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sterne JAC, Murthy S, Diaz JV, et al. ; WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group . Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2020;324(13):1330-1341. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17023 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

