Trainee Physician Milestone Ratings and Patient Complaints in Early Posttraining Practice
- PMID: 37040112
- PMCID: PMC10091163
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.7588
Trainee Physician Milestone Ratings and Patient Complaints in Early Posttraining Practice
Abstract
Importance: Evaluation of trainees in graduate medical education training programs using Milestones has been in place since 2013. It is not known whether trainees who have lower ratings during the last year of training go on to have concerns related to interactions with patients in posttraining practice.
Objective: To investigate the association between resident Milestone ratings and posttraining patient complaints.
Design, setting, and participants: This retrospective cohort study included physicians who completed Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME)-accredited programs between July 1, 2015, and June 30, 2019, and worked at a site that participated in the national Patient Advocacy Reporting System (PARS) program for at least 1 year. Milestone ratings from ACGME training programs and patient complaint data from PARS were collected. Data analysis was conducted from March 2022 to February 2023.
Exposures: Lowest professionalism (P) and interpersonal and communication skills (ICS) Milestones ratings 6 months prior to the end of training.
Main outcomes and measures: PARS year 1 index scores, based on recency and severity of complaints.
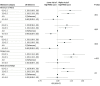
Results: The cohort included 9340 physicians with median (IQR) age of 33 (31-35) years; 4516 (48.4%) were women physicians. Overall, 7001 (75.0%) had a PARS year 1 index score of 0, 2023 (21.7%) had a score of 1 to 20 (moderate), and 316 (3.4%) had a score of 21 or greater (high). Among physicians in the lowest Milestones group, 34 of 716 (4.7%) had high PARS year 1 index scores, while 105 of 3617 (2.9%) with Milestone ratings of 4.0 (proficient), had high PARS year 1 index scores. In a multivariable ordinal regression model, physicians in the 2 lowest Milestones rating groups (0-2.5 and 3.0-3.5) were statistically significantly more likely to have higher PARS year 1 index scores than the reference group with Milestones ratings of 4.0 (0-2.5 group: odds ratio, 1.2 [95% CI, 1.0-1.5]; 3.0-3.5 group: odds ratio, 1.2 [95% CI, 1.1-1.3]).
Conclusions and relevance: In this study, trainees with low Milestone ratings in P and ICS near the end of residency were at increased risk for patient complaints in their early posttraining independent physician practice. Trainees with lower Milestone ratings in P and ICS may need more support during graduate medical education training or in the early part of their posttraining practice career.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

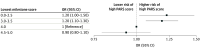

Comment in
-
Competency-Based Medical Education-A Journey or a Destination?JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Apr 3;6(4):e237395. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.7395. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37040120 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hamstra SJ, Yamazaki K, Shah HA, et al. . Milestones National Report 2019. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/PDFs/Milestones/2019MilestonesNationa...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

