Extent of use of artificial intelligence & machine learning protocols in cancer diagnosis: A scoping review
- PMID: 37040222
- PMCID: PMC10284367
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_555_20
Extent of use of artificial intelligence & machine learning protocols in cancer diagnosis: A scoping review
Abstract
Background & objectives: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have shown promising results in cancer diagnosis in validation tests involving retrospective patient databases. This study was aimed to explore the extent of actual use of AI/ML protocols for diagnosing cancer in prospective settings.
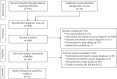
Methods: PubMed was searched for studies reporting usage of AI/ML protocols for cancer diagnosis in prospective (clinical trial/real world) setting with the AI/ML diagnosis aiding clinical decision-making, from inception till May 17, 2021. Data pertaining to the cancer, patients and the AI/ML protocol were extracted. Comparison of AI/ML protocol diagnosis with human diagnosis was recorded. Through a post hoc analysis, data from studies describing validation of various AI/ML protocols were extracted.
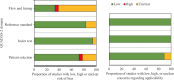
Results: Only 18/960 initial hits (1.88%) utilized AI/ML protocols for diagnostic decision-making. Most protocols used artificial neural network and deep learning. AI/ML protocols were utilized for cancer screening, pre-operative diagnosis and staging and intra-operative diagnosis of surgical specimens. The reference standard for 17/18 studies was histology. AI/ML protocols were used to diagnose cancers of the colorectum, skin, uterine cervix, oral cavity, ovaries, prostate, lungs and brain. AI/ML protocols were found to improve human diagnosis, and had either similar or better performance than the human diagnosis, especially made by the less experienced clinician. Validation of AI/ML protocols was described by 223 studies of which only four studies were from India. Also there was a huge variation in the number of items used for validation.
Interpretation & conclusions: The findings of this review suggest that a meaningful translation from the validation of AI/ML protocols to their actual usage in cancer diagnosis is lacking. Development of regulatory framework specific for AI/ML usage in healthcare is essential.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; diagnosis; machine learning; neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence for the Prediction and Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Mar 31;25:e44248. doi: 10.2196/44248. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37000507 Free PMC article.
-
Role of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning models in corneal disorders - A narrative review.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2024 Sep;47(7):104242. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2024.104242. Epub 2024 Jul 15. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2024. PMID: 39013268 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Head and Neck Cancer: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews.Adv Ther. 2023 Aug;40(8):3360-3380. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02527-9. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37291378 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Artificial Intelligence in the Identification and Diagnosis of Frailty Syndrome in Older Adults: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Oct 20;25:e47346. doi: 10.2196/47346. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37862082 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of artificial intelligence in urologic oncology.Investig Clin Urol. 2024 May;65(3):202-216. doi: 10.4111/icu.20230435. Investig Clin Urol. 2024. PMID: 38714511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intelligent medicine in focus: the 5 stages of evolution in robot-assisted surgery for prostate cancer in the past 20 years and future implications.Mil Med Res. 2024 Aug 21;11(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00566-z. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39164787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraoperative Imaging and Optical Visualization Techniques for Brain Tumor Resection: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;15(19):4890. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194890. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Application of Artificial Intelligence to Cancer Research: A Comprehensive Guide.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241250324. doi: 10.1177/15330338241250324. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38775067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating multimodal imaging and peritumoral features for enhanced prostate cancer diagnosis: A machine learning approach.PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0323752. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323752. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40373044 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Decision-Making in Healthcare: A Thematic Analysis of a Systematic Review of Reviews.Health Serv Res Manag Epidemiol. 2024 Mar 5;11:23333928241234863. doi: 10.1177/23333928241234863. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Health Serv Res Manag Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38449840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A, Gerendas BS, Waldstein SM, Bogunović H. Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018;67:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Kann BH, Thompson R, Thomas CR, Jr, Dicker A, Aneja S. Artificial intelligence in oncology: Current applications and future directions. Oncology (Williston Park) 2019;33:46–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical