Genomic surveillance uncovers a pandemic clonal lineage of the wheat blast fungus
- PMID: 37040332
- PMCID: PMC10089362
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002052
Genomic surveillance uncovers a pandemic clonal lineage of the wheat blast fungus
Erratum in
-
Correction: Genomic surveillance uncovers a pandemic clonal lineage of the wheat blast fungus.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jul 19;21(7):e3002236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002236. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 39417205 Free PMC article.
Abstract
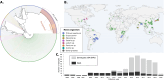
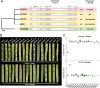
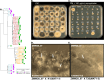
Wheat, one of the most important food crops, is threatened by a blast disease pandemic. Here, we show that a clonal lineage of the wheat blast fungus recently spread to Asia and Africa following two independent introductions from South America. Through a combination of genome analyses and laboratory experiments, we show that the decade-old blast pandemic lineage can be controlled by the Rmg8 disease resistance gene and is sensitive to strobilurin fungicides. However, we also highlight the potential of the pandemic clone to evolve fungicide-insensitive variants and sexually recombine with African lineages. This underscores the urgent need for genomic surveillance to track and mitigate the spread of wheat blast outside of South America and to guide preemptive wheat breeding for blast resistance.
Copyright: © 2023 Latorre et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
We have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: KL is a founder of Floodlight Genomics, TI receives funding from Krishi Gobeshona Foundation of Bangladesh, and SK receives funding from industry and has filed patents on plant disease resistance.
Figures

Comment in
-
Genomic surveillance urgently needed to control wheat blast pandemic spreading across continents.PLoS Biol. 2023 Apr 12;21(4):e3002090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002090. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37043438 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Genomic surveillance urgently needed to control wheat blast pandemic spreading across continents.PLoS Biol. 2023 Apr 12;21(4):e3002090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002090. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37043438 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of wheat blast resistance gene Rmg8 accompanied by differentiation of variants recognizing the powdery mildew fungus.Nat Plants. 2024 Jun;10(6):971-983. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01711-1. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Nat Plants. 2024. PMID: 38898164
-
Breeding of a Near-Isogenic Wheat Line Resistant to Wheat Blast at Both Seedling and Heading Stages Through Incorporation of Rmg8.Phytopathology. 2024 Aug;114(8):1843-1850. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-07-23-0234-R. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Phytopathology. 2024. PMID: 38776064
-
Wheat spike blast: genetic interventions for effective management.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5483-5494. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07356-7. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35478296 Review.
-
Wheat genetic resources have avoided disease pandemics, improved food security, and reduced environmental footprints: A review of historical impacts and future opportunities.Glob Chang Biol. 2024 Aug;30(8):e17440. doi: 10.1111/gcb.17440. Glob Chang Biol. 2024. PMID: 39185562 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc-finger (ZiF) fold secreted effectors form a functionally diverse family across lineages of the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jun 17;20(6):e1012277. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012277. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38885263 Free PMC article.
-
Rmg8 gene against wheat blast.Nat Plants. 2024 Jun;10(6):836-837. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01690-3. Nat Plants. 2024. PMID: 38898163 No abstract available.
-
Bioengineering a plant NLR immune receptor with a robust binding interface toward a conserved fungal pathogen effector.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 9;121(28):e2402872121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2402872121. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38968126 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Structural Genomics Unravels Common Folds and Novel Families in the Secretome of Fungal Phytopathogen Magnaporthe oryzae.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021 Nov;34(11):1267-1280. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-21-0071-R. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021. PMID: 34415195 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional landscape of plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae reveals distinct families of temporally co-regulated and structurally conserved effectors.Plant Cell. 2023 Apr 20;35(5):1360-1385. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad036. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36808541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global genomic surveillance strategy for pathogens with pandemic and epidemic potential (Draft). WHO; 2022. –2032. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2021/12/08/default-calendar/.... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/J/000PR9796/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/R01356X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/P023339/1 /BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/W008157/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000PR9795/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

