The Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus GG Therapy on Liver and Drinking Assessments in Patients with Moderate Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis
- PMID: 37040544
- PMCID: PMC10524173
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002283
The Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus GG Therapy on Liver and Drinking Assessments in Patients with Moderate Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis
Abstract
Introduction: We investigated the effect of daily oral Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in reducing liver injury/severity and drinking in patients with alcohol use disorder and moderately severe alcohol-associated hepatitis.
Methods: Forty-six male and female individuals with alcohol use disorder and moderate alcohol-associated hepatitis (12 ≤ model for end-stage liver disease score < 20, aged 21-67 years) received either LGG (n = 24) or placebo (n = 22). Data were collected/assessed at baseline and at 1, 3, and 6 months.
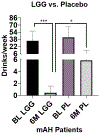
Results: LGG treatment was associated with a significant reduction in liver injury after 1 month. Six months of LGG treatment reduced heavy drinking levels to social or abstinence levels.
Discussion: LGG treatment was associated with an improvement in both liver injury and drinking.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01922895.
Copyright © 2023 by The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
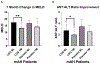
References
-
- Szabo G and Lippai D, Converging actions of alcohol on liver and brain immune signaling. International review of neurobiology, 2014. 118: p. 359–380. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt C, Thinking from the Gut. Nature, 2015. 518(7540): p. S12–S14. - PubMed
-
- Crabb DW, et al., Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcohol-Associated Liver Diseases: 2019 Practice Guidance From the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 2020. 71(1): p. 306–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

