Positive selection of somatically mutated clones identifies adaptive pathways in metabolic liver disease
- PMID: 37040760
- PMCID: PMC10321862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.014
Positive selection of somatically mutated clones identifies adaptive pathways in metabolic liver disease
Abstract
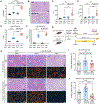
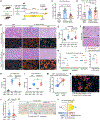
Somatic mutations in nonmalignant tissues accumulate with age and injury, but whether these mutations are adaptive on the cellular or organismal levels is unclear. To interrogate genes in human metabolic disease, we performed lineage tracing in mice harboring somatic mosaicism subjected to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Proof-of-concept studies with mosaic loss of Mboat7, a membrane lipid acyltransferase, showed that increased steatosis accelerated clonal disappearance. Next, we induced pooled mosaicism in 63 known NASH genes, allowing us to trace mutant clones side by side. This in vivo tracing platform, which we coined MOSAICS, selected for mutations that ameliorate lipotoxicity, including mutant genes identified in human NASH. To prioritize new genes, additional screening of 472 candidates identified 23 somatic perturbations that promoted clonal expansion. In validation studies, liver-wide deletion of Tbx3, Bcl6, or Smyd2 resulted in protection against hepatic steatosis. Selection for clonal fitness in mouse and human livers identifies pathways that regulate metabolic disease.
Keywords: Gpam; Mboat7; NAFLD; NASH; Smyd2; Tbx3; chronic liver disease; fatty liver disease; in vivo screening; somatic mosaicism.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Y.H. consults for Helio Genomics, Espervita Therapeutics, and Roche Diagnostics. Y.H. is a shareholder of Alentis Therapeutics and Espervita Therapeutics. M.H. consults for Spliceor, is on the speakers panel for Boston Scientific, and has research support from Pfizer and AstraZeneca. H.Z. consults for Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Jumble Therapeutics, and Chroma Medicines, and serves on the SAB of Ubiquitix. H.Z. has research support from Chroma Medicines. H.Z. owns stock in Ionis and Madrigal Pharmaceuticals. M.H., H.Z., and P.C. consult for FL86 and Flagship Pioneering. M.H. and P.C. are co-inventors on patents on somatic mutants in liver disease, including ACVR2A and GPAM. Z.W., H.Z., and L.L. are co-inventors on patents on GPAM, TBX3, and SMYD2 siRNAs.
Figures





Update of
-
Positive selection of somatically mutated clones identifies adaptive pathways in metabolic liver disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 21:2023.03.20.533505. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.20.533505. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell. 2023 Apr 27;186(9):1968-1984.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.014. PMID: 36993727 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Survival of the Fittest: Clonal Selection of Somatic Mutations Reveals Targets to Abate Chronic Liver Injury.Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):936-937. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.002. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Gastroenterology. 2024. PMID: 38340873 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

