Anti-CD20 antibodies and bendamustine attenuate humoral immunity to COVID-19 vaccination in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 37041299
- PMCID: PMC10089694
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-023-05204-7
Anti-CD20 antibodies and bendamustine attenuate humoral immunity to COVID-19 vaccination in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
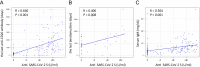
Serologic responses of COVID-19 vaccine are impaired in patients with B-cell lymphoma, especially those who had recently been treated with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. However, it is still unclear whether those patients develop an immune response following vaccination. We investigated the efficacy of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in 171 patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) who received two doses of an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine and we compared the efficacy of vaccination to that in 166 healthy controls. Antibody titers were measured 3 months after administration of the second vaccine dose. Patients with B-NHL showed a significantly lower seroconversion rate and a lower median antibody titer than those in healthy controls. The antibody titers showed correlations with the period from the last anti-CD20 antibody treatment to vaccination, the period from the last bendamustine treatment to vaccination and serum IgM level. The serologic response rates and median antibody titers were significantly different between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients in whom anti-CD20 antibody treatment was completed within 9 months before vaccination and follicular lymphoma (FL) patients in whom anti-CD20 antibody treatment was completed within 15 months before vaccination. Moreover, the serologic response rates and median antibody titers were significantly different among FL patients in whom bendamustine treatment was completed within 33 months before vaccination. We demonstrated that B-NHL patients who were recently treated with anti-CD20 antibodies and bendamustine had a diminished humoral response to COVID-19 vaccination. UMIN 000,045,267.
Keywords: Anti-CD20 antibodies; B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL); Bendamustine; COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mehta V, Goel S, Kabarriti R, Cole D, Goldfinger M, Acuna-Villaorduna A, Pradhan K, Thota R, Reissman S, Sparano JA, Gartrell BA, Smith RV, Ohri N, Garg M, Racine AD, Kalnicki S, Perez-Soler R, Halmos B, Verma A. Case fatality rate of cancer patients with COVID-19 in a New York hospital system. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(7):935–941. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee LYW, Cazier JB, Starkey T, Briggs SEW, Arnold R, Bisht V, Booth S, Campton NA, Cheng VWT, Collins G, Curley HM, Earwaker P, Fittall MW, Gennatas S, Goel A, Hartley S, Hughes DJ, Kerr D, Lee AJX, Lee RJ, Lee SM, McKenzie H, Middleton CP, Murugaesu N, Newsom-Davis T, Olsson-Brown AC, Palles C, Powles T, Protheroe EA, Purshouse K, Sharma-Oates A, Sivakumar S, Smith AJ, Topping O, Turnbull CD, Varnai C, Briggs ADM, Middleton G, Kerr R, Team UKCCMP COVID-19 prevalence and mortality in patients with cancer and the effect of primary tumour subtype and patient demographics: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(10):1309–1316. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30442-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vijenthira A, Gong IY, Fox TA, Booth S, Cook G, Fattizzo B, Martin-Moro F, Razanamahery J, Riches JC, Zwicker J, Patell R, Vekemans MC, Scarfo L, Chatzikonstantinou T, Yildiz H, Lattenist R, Mantzaris I, Wood WA, Hicks LK. Outcomes of patients with hematologic malignancies and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 3377 patients. Blood. 2020;136(25):2881–2892. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Passamonti F, Cattaneo C, Arcaini L, Bruna R, Cavo M, Merli F, Angelucci E, Krampera M, Cairoli R, Della Porta MG, Fracchiolla N, Ladetto M, Gambacorti Passerini C, Salvini M, Marchetti M, Lemoli R, Molteni A, Busca A, Cuneo A, Romano A, Giuliani N, Galimberti S, Corso A, Morotti A, Falini B, Billio A, Gherlinzoni F, Visani G, Tisi MC, Tafuri A, Tosi P, Lanza F, Massaia M, Turrini M, Ferrara F, Gurrieri C, Vallisa D, Martelli M, Derenzini E, Guarini A, Conconi A, Cuccaro A, Cudillo L, Russo D, Ciambelli F, Scattolin AM, Luppi M, Selleri C, Ortu La Barbera E, Ferrandina C, Di Renzo N, Olivieri A, Bocchia M, Gentile M, Marchesi F, Musto P, Federici AB, Candoni A, Venditti A, Fava C, Pinto A, Galieni P, Rigacci L, Armiento D, Pane F, Oberti M, Zappasodi P, Visco C, Franchi M, Grossi PA, Bertu L, Corrao G, Pagano L, Corradini P, Investigators I-H-C. Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity in patients with haematological malignancies in Italy: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(10):e737–e745. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30251-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wood WA, Neuberg DS, Thompson JC, Tallman MS, Sekeres MA, Sehn LH, Anderson KC, Goldberg AD, Pennell NA, Niemeyer CM, Tucker E, Hewitt K, Plovnick RM, Hicks LK. Outcomes of patients with hematologic malignancies and COVID-19: a report from the ASH Research Collaborative Data Hub. Blood Adv. 2020;4(23):5966–5975. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

