Coronary computed tomography angiography study on the relationship between the Ramus Intermedius and Atherosclerosis in the bifurcation of the left main coronary artery
- PMID: 37041479
- PMCID: PMC10091592
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-023-01009-2
Coronary computed tomography angiography study on the relationship between the Ramus Intermedius and Atherosclerosis in the bifurcation of the left main coronary artery
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the relationship between the ramus intermedius (RI) and atherosclerosis in the bifurcation of the left coronary artery (LCA).
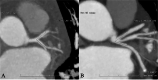
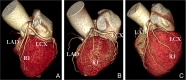
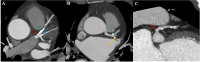
Methods: Screening patients who underwent CCTA from January to September 2021, 100 patients with RI (RI group) and 100 patients without RI (no-RI group) were randomly enrolled, Evaluation of RI distribution characteristics and left main coronary artery(LM),Left anterior descending branch(LAD),left circumflex branch(LCX) proximal segment plaque distribution, measurement of LAD-LCX bifurcation angle(∠LAD-LCX),Comparison of the three distribution characteristics with the incidence of plaques in the left main trunk bifurcation area (LM, LAD, LCX) between groups and within the RI group.
Results: The difference in the incidence of plaques in the proximal LCX and the LM between the RI group and the no-RI group were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). The incidence of plaques in the proximal LAD in the RI group was significantly higher than that in the non-RI group (77% versus 53%, P < 0.05). However, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups after PSM. A univariate logistic regression analysis revealed that an RI was a risk factor for plaque formation in the proximal LAD (P < 0.001), and a multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that an RI was not an independent risk factor for plaque formation in the proximal LAD (P > 0.05). When compared within the RI group, the difference in the incidence of plaques in the proximal segment of LAD, the proximal segment of LCX, and the LM among the different distribution groups of RI was not statistically significant, respectively (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: RI is not an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis in the left coronary artery bifurcation zone, but it may indirectly increase the risk of atherosclerosis in the proximal segment of the LAD.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Bifurcation angle; Coronary computed tomography angiography; Ramus intermedius.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A coronary computed tomography angiography study on anatomical characteristics of the diagonal branch of anterior interventricular artery.Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2023;82(4):822-829. doi: 10.5603/FM.a2022.0100. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2023. PMID: 36472396
-
Quantification of left coronary bifurcation angles and plaques by coronary computed tomography angiography for prediction of significant coronary stenosis: A preliminary study with dual-source CT.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 27;12(3):e0174352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174352. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28346530 Free PMC article.
-
Association between bifurcation angle of the left main coronary artery and severity of stenosis of the proximal left anterior descending artery.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2023 May-Jun 23;34(2):93-97. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2022-031. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2023. PMID: 35976685 Free PMC article.
-
The role of septal perforators and "myocardial bridging effect" in atherosclerotic plaque distribution in the coronary artery disease.Pol J Radiol. 2015 Apr 16;80:195-201. doi: 10.12659/PJR.893227. eCollection 2015. Pol J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25922625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Relationship between Left Coronary Artery Bifurcation Angle and Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 31;11(17):5143. doi: 10.3390/jcm11175143. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36079071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Left Main Coronary Artery Disease: A Contemporary Review of Diagnosis and Management.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 18;25(2):66. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2502066. eCollection 2024 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39077332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ramus Intermedius: A Bridge to Survival in the Setting of Triple-Vessel Total Occlusion.Cureus. 2024 May 29;16(5):e61288. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61288. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38947610 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of the Presence of the Ramus Intermedius on Atherosclerosis Plaque Deposition in the Left Bifurcation Region in Low-Risk Individuals.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Feb 13;26(2):25252. doi: 10.31083/RCM25252. eCollection 2025 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40026505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OPOLSKI M P, GRODECKI K, STARUCH A D, et al. Accuracy of RESOLVE score derived from coronary computed tomography versus visual angiography to predict side branch occlusion in percutaneous bifurcation intervention. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2020;14(3):258–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2019.11.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- CHEN X, DAI J, LIN J et al. Image-based morphometric studies of human coronary artery bifurcations with/without coronary artery disease.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin, 2020:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

