RA-RAR signaling promotes mouse vaginal opening through increasing β-catenin expression and vaginal epithelial cell apoptosis
- PMID: 37041518
- PMCID: PMC10088237
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-023-01084-8
RA-RAR signaling promotes mouse vaginal opening through increasing β-catenin expression and vaginal epithelial cell apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Retinoic acid (RA) plays important role in the maintenance and differentiation of the Müllerian ducts during the embryonic stage via RA receptors (RARs). However, the function and mechanism of RA-RAR signaling in the vaginal opening are unknown.
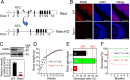
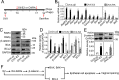
Method: We used the Rarα knockout mouse model and the wild-type ovariectomized mouse models with subcutaneous injection of RA (2.5 mg/kg) or E2 (0.1 µg/kg) to study the role and mechanism of RA-RAR signaling on the vaginal opening. The effects of Rarα deletion on Ctnnb1 mRNA levels and cell apoptosis in the vaginas were analyzed by real-time PCR and immunofluorescence, respectively. The effects of RA on the expression of β-catenin and apoptosis in the vaginas were analyzed by real-time PCR and western blotting. The effects of E2 on RA signaling molecules were analyzed by real-time PCR and western blotting.
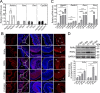
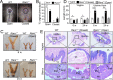
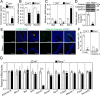
Results: RA signaling molecules were expressed in vaginal epithelial cells, and the mRNA and/or protein levels of RALDH2, RALDH3, RARα and RARγ reached a peak at the time of vaginal opening. The deletion of Rarα resulted in 25.0% of females infertility due to vaginal closure, in which the mRNA (Ctnnb1, Bak and Bax) and protein (Cleaved Caspase-3) levels were significantly decreased, and Bcl2 mRNA levels were significantly increased in the vaginas. The percentage of vaginal epithelium with TUNEL- and Cleaved Caspase-3-positive signals were also significantly decreased in Rarα-/- females with vaginal closure. Furthermore, RA supplementation of ovariectomized wild-type (WT) females significantly increased the expression of β-catenin, active β-catenin, BAK and BAX, and significantly decreased BCL2 expression in the vaginas. Thus, the deletion of Rarα prevents vaginal opening by reducing the vaginal β-catenin expression and epithelial cell apoptosis. The deletion of Rarα also resulted in significant decreases in serum estradiol (E2) and vagina Raldh2/3 mRNA levels. E2 supplementation of ovariectomized WT females significantly increased the expression of RA signaling molecules in the vaginas, suggesting that the up-regulation of RA signaling molecules in the vaginas is dependent on E2 stimulation.
Conclusion: Taken together, we propose that RA-RAR signaling in the vaginas promotes vaginal opening through increasing β-catenin expression and vaginal epithelial cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Mouse; Retinoic acid receptor; Vaginal opening; β-catenin.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinoic acid signaling determines the fate of uterine stroma in the mouse Müllerian duct.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 13;113(50):14354-14359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608808113. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27911779 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of retinoic acid receptors alpha and gamma into neoplastic epidermal cells causes retinoic acid-induced growth arrest and apoptosis.Carcinogenesis. 2001 Dec;22(12):1955-63. doi: 10.1093/carcin/22.12.1955. Carcinogenesis. 2001. PMID: 11751425
-
[Paeoniflorin inhibits Wnt1/β-catenin pathway and promotes apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by upregulating lncRNA MALAT1].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Aug;38(8):692-698. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35851082 Chinese.
-
Sequence analysis of retinoic acid receptor alpha, beta and gamma isoforms in the lizard, Podarcis sicula.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 May;104(3-5):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17449240
-
F9 embryocarcinoma cells: a cell autonomous model to study the functional selectivity of RARs and RXRs in retinoid signaling.Histol Histopathol. 2001 Jul;16(3):909-22. doi: 10.14670/HH-16.909. Histol Histopathol. 2001. PMID: 11510982 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

