Effect of EIT-guided PEEP titration on prognosis of patients with moderate to severe ARDS: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 37041561
- PMCID: PMC10088128
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07280-6
Effect of EIT-guided PEEP titration on prognosis of patients with moderate to severe ARDS: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acute respiratory syndrome distress (ARDS) is a clinical common syndrome with high mortality. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT)-guided positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) titration can achieve the compromise between lung overdistension and collapse which may minimize ventilator-induced lung injury in these patients. However, the effect of EIT-guided PEEP titration on the clinical outcomes remains unknown. The objective of this trial is to investigate the effects of EIT-guided PEEP titration on the clinical outcomes for moderate or severe ARDS, compared to the low fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2)-PEEP table.
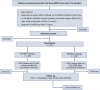
Methods: This is a prospective, multicenter, single-blind, parallel-group, adaptive designed, randomized controlled trial (RCT) with intention-to-treat analysis. Adult patients with moderate to severe ARDS less than 72 h after diagnosis will be included in this study. Participants in the intervention group will receive PEEP titrated by EIT with a stepwise decrease PEEP trial, whereas participants in the control group will select PEEP based on the low FiO2-PEEP table. Other ventilator parameters will be set according to the ARDSNet strategy. Participants will be followed up until 28 days after enrollment. Three hundred seventy-six participants will be recruited based on a 15% decrease of 28-day mortality in the intervention group, with an interim analysis for sample size re-estimation and futility assessment being undertaken once 188 participants have been recruited. The primary outcome is 28-day mortality. The secondary outcomes include ventilator-free days and shock-free days at day 28, length of ICU and hospital stay, the rate of successful weaning, proportion requiring rescue therapies, compilations, respiratory variables, and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA).
Discussion: As a heterogeneous syndrome, ARDS has different responses to treatment and further results in different clinical outcomes. PEEP selection will depend on the properties of patients and can be individually achieved by EIT. This study will be the largest randomized trial to investigate thoroughly the effect of individual PEEP titrated by EIT in moderate to severe ARDS patients to date.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrial.gov NCT05207202. First published on January 26, 2022.
Keywords: Acute respiratory syndrome distress; Clinical trial; Electrical impedance tomography; Mechanical ventilation; Positive end-expiratory pressure.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early individualized positive end-expiratory pressure guided by electrical impedance tomography in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Crit Care. 2021 Jun 30;25(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03645-y. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34193224 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multicentre, parallel, open-label, two-arm, randomised controlled trial on the prognosis of electrical impedance tomography-guided versus low PEEP/FiO2 table-guided PEEP setting: a trial protocol.BMJ Open. 2024 Feb 1;14(2):e080828. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080828. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38307528 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical impedance tomography for titration of positive end-expiratory pressure in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Crit Care. 2022 Nov 4;26(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04201-y. Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 36333809 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical impedance tomography-guided positive end-expiratory pressure titration in ARDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Intensive Care Med. 2024 May;50(5):617-631. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07362-2. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Intensive Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38512400 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical impedance tomography guided positive end-expiratory pressure titration in critically ill and surgical adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Nov 23;24(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03394-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39580405 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in cardiorespiratory monitoring in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients.J Intensive Care. 2024 May 5;12(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40560-024-00727-1. J Intensive Care. 2024. PMID: 38706001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrical impedance tomography to set positive end-expiratory pressure.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2025 Jun 1;31(3):319-327. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000001255. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 39976222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrical impedance tomography for PEEP titration in ARDS patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Monit Comput. 2025 Feb 26. doi: 10.1007/s10877-025-01266-2. Online ahead of print. J Clin Monit Comput. 2025. PMID: 40011398 Review.
References
-
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA. 2016;315(8):788–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2504405/National Key R&D Program of China
- BE2020786/the Clinical Science and Technology Specific Projects of Jiangsu Province
- 81870066/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82270083/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LGY2022025/the Second Level Talents of the "333 High Level Talents Training Project" in the sixth phase in Jiangsu
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

