Intercellular adhesion molecule 4 and ischemic stroke: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 37041579
- PMCID: PMC10091569
- DOI: 10.1186/s12959-023-00485-4
Intercellular adhesion molecule 4 and ischemic stroke: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
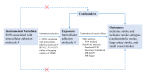
Background: Experimental studies suggested that intercellular adhesion molecule 4 (ICAM-4) might be implicated in ischemic stroke, but the population-based evidence on the relationship between ICAM-4 and ischemic stroke were limited. Herein, we performed a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to investigate the associations of genetically determined plasma ICAM-4 with the risks of ischemic stroke and its subtypes.
Methods: A total of 11 single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with ICAM-4 were selected as instrumental variables based on the genome-wide association studies (GWAS) with 3,301 European individuals. Summary-level data about ischemic stroke and its subtypes were obtained from the Multi-ancestry GWAS launched by the International Stroke Genetics Consortium. We used the inverse-variance weighted method followed by a series of sensitivity analyses to evaluate the associations of genetically determined ICAM-4 with the risks of ischemic stroke and its subtypes.
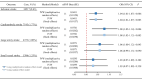
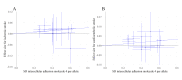
Results: Genetically determined higher ICAM-4 levels were significantly associated with increased risks of ischemic stroke (in the IVW method fitted to multiplicative random effects model: odds ratio [OR] per standard deviation [SD] increase, 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.07; P = 0.006; in the IVW analysis with fixed effects model: OR per SD increase, 1.04; 95% CI, 1.01-1.07; P = 0.003) and cardioembolic stroke (in multiplicative random effects model: OR per SD increase, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.02-1.14; P = 0.004; in fixed effects model: OR per SD increase, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.13; P = 0.003). There was no association of ICAM-4 with the risks of large artery stroke and small vessel stroke. MR-Egger regression showed no directional pleiotropy for all associations, and the sensitivity analyses with different MR methods further confirmed these findings.
Conclusions: We found positive associations of genetically determined plasma ICAM-4 with the risks of ischemic stroke and cardioembolic stroke. Future studies are needed to explore the detailed mechanism and investigate the targeting effect of ICAM-4 on ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Intercellular adhesion molecule 4; Ischemic stroke; Mendelian randomization; Risk.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Feske SK. Ischemic stroke. Am J Med. Dec 2021;134(12):1457–64. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.07.027. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

